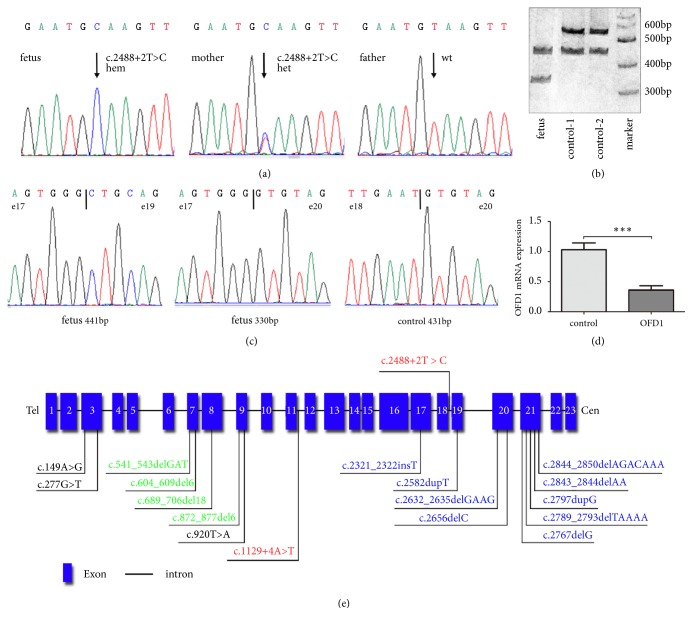
Figure 2.
Molecular findings from sequencing, OFD1 expression assessment, and the distribution of mutations found to cause JBTS10. (a) Sanger sequencing showed a hemizygous splice variant (c.2488+2T>C, NM_003611.2) in the OFD1 gene in the index fetus, while heterozygous in the mother and absent in the father. (b) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed spanning exon amplification products in the index fetus and two male healthy controls. The controls displayed two bands, 431-bp and 541-bp, respectively. The index fetus had additional two bands, 441-bp and 330-bp, respectively. (c) Sanger sequencing showed that exon 19 was skipped in the 431-bp product from the healthy controls, which was confirmed to come from other normal transcript variants. In the affected fetus exon 18 was skipped in the 441-bp product, while exons 18 and 19 were both skipped in the 330-bp product (d) The qPCR result reveals the decrease of total OFD1 mRNA in the index fetus. ∗∗∗ P < 0.001 (independent t -test). (e) Gene structure of OFD1 and the distribution of mutations found to cause JBTS10. The blocks indicate the gene exons. All the mutations are collected from HGMD. The mutations marked with blue, green, black, and red correspond to frame-shift, in-frame, missense, and splicing mutations, respectively. Upper: the identified mutation in this study.