Figure 1.
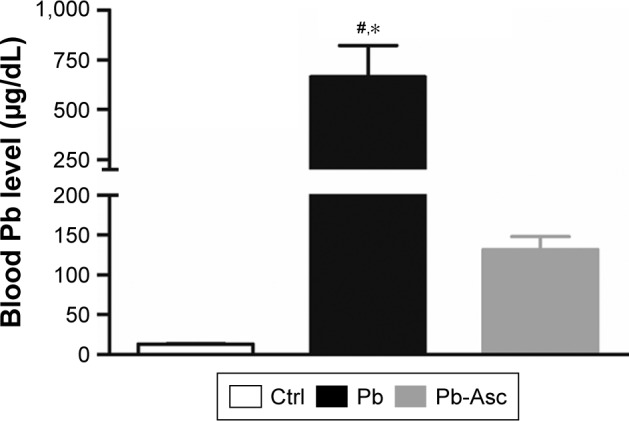
Ascorbate supplementation reduces the elevation in blood Pb levels induced by chronic Pb treatment through drinking.
Notes: Significant increase in blood Pb levels of pups of the Pb group (665.5±384.6; mean ± SD) was observed when compared to those of the Ctrl group (13.07±1.332; mean ± SD). Ascorbate supplementation reduced the blood Pb levels of Pb exposed pups to 131.8±39.53 (mean ± SD). Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n=6 rats per group). *,#Statistical significance when compared to Ctrl and Pb-Asc groups, respectively (P<0.0001; F=36.27; ANOVA with Newman–Keuls correction).
Abbreviations: Asc, ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean.
