Figure 5.
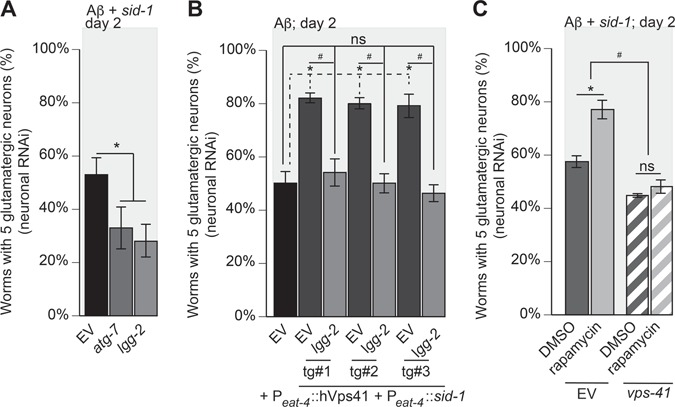
Vps41-mediated neuroprotection from Aβ-induced neurodegeneration is dependent on autophagy. (A) RNAi depletion of atg-7 or lgg-2 was performed specifically within neurons of C. elegans that also express Aβ in strain UA338 (baIn34[Peat-4:: Aβ,Pmyo-2::mCherry]; adIs1240[Peat-4::GFP]; sid-1(pk3321); uIS69 [Pmyo-2::mCherry; Punc-119::sid-1]). Here, there was a significantly increased neurodegeneration compared to the EV RNAi control (P = 0.008; P = 0.003; one-way ANOVA with a Fisher’s LSD test; n = 90 for both). (B) Worms overexpressing Aβ and GFP in glutamatergic neurons, designated as strain UA337 (baIn34[Peat-4:: Aβ,Pmyo-2::mCherry]; adIs1240[Peat-4::GFP]; sid-1(pk3321)), exhibit significant degeneration that was rescued with the overexpression of hVps41 and sid-1 following the creation of the RNAi-sensitive strain (UA329 (baEx195[Peat-4::hVps41, Peat-4::sid-1, Punc-54::tdTomato]; baIn34[Peat-4:: Aβ,Pmyo-2::mCherry]; adIs1240[Peat-4::GFP]; sid-1(pk3321)). In this background, overexpression of hVps41 significantly (*) rescues Aβ neurodegeneration compared to Aβ control when treated with EV RNAi in all three transgenic lines [tg#1 P = 0.0008; tg#2 P = 0.0008; tg#3 P = 0.0058]. RNAi depletion of lgg-2 in these transgenic lines negates (ns) the rescuing phenotype of hVps41 overexpression in all three transgenic lines when compared to Aβ alone [tg#1 P = 0.972; tg#2 P > 0.999; tg#3 P = 0.992]. The knockdown of lgg-2 in the hVps41 background also reduced glutamatergic neuronal rescue significantly (#) in all three transgenic lines [tg#1 P = 0.004; tg#2 P = 0.0005; tg#3 P = 0.002 (F(6,14) = 17.13; n = 90 for each line; one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s post hoc analysis)]. (C) RNAi knockdown of EV or vps-41 was performed specifically within glutamatergic neurons of C. elegans that also express Aβ in strain UA338 ((baIn34[Peat-4:: Aβ,Pmyo-2::mCherry]; adIs1240[Peat-4::GFP]; sid-1(pk3321); uIS69 [Pmyo-2::mCherry; Punc-119::sid-1]). Worms were then treated with 0.5 μM rapamycin in 0.01% DMSO or 0.01% DMSO only. In the EV RNAi control, treatment with rapamycin significantly (*) reduced neurodegeneration (F(3,8) = 39.13; P = 0.002), whereas in animals treated with vps-41 RNAi, rapamycin exposure does not rescue neurodegeneration (P = 0.745). Consistent with previous observations, vps-41 RNAi increased (#) neurodegeneration compared to EV RNAi control (P = 0.0197; one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s post-hoc analysis; n = 90 for each treatment). These data are reported as mean + S.D. while * and # denote statistical significance as detailed within each section of this legend.
