Figure 6.
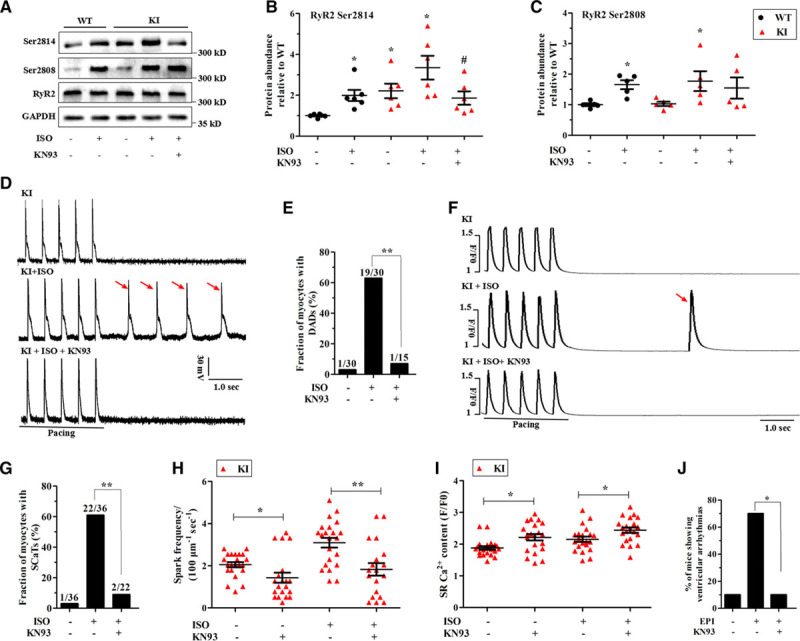
CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of RyR2 and functional effects of CaMKII inhibition in KI hearts. A through C, Representative immunoblots (A) and quantitative assessment of the protein and phosphorylation levels of RyR2 at Ser2814 (B; *P<0.05 versus WT at baseline, #P<0.05 versus KI+ISO; n=6 hearts/genotype) and Ser2808 (C; *P<0.05 versus WT at baseline; n=5 hearts/genotype) from left ventricle sections in littermates of WT and KI perfused hearts±1 μM ISO or 1 μM KN93. D and E, Representative traces of the action potentials (D) and cumulative incidence of DADs (E; **P<0.01) after a stimulation pause after a 2-Hz field stimulation in KI cardiomyocytes±1 μM ISO or 1 μM KN93. F and G, Representative traces of SCaTs (F) and the cumulative incidence of SCaTs (G; **P<0.01) after a stimulation pause after a 2-Hz field stimulation in KI cardiomyocytes±1 μM ISO or 1 μM KN93. H, Cumulative data of Ca2+ spark frequency in KI cardiomyocytes±ISO (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). I, Cumulative data of caffeine-induced Ca2+ transient amplitude (ie, SR Ca2+ content) in KI cardiomyocytes±ISO (*P<0.05). J, Cumulative incidence of ventricular arrhythmias in KN93-pretreated KI mice after an intraperitoneal injection of 2 mg/kg epinephrine (*P<0.05; n=10 KI mice for each group). CaMKII indicates calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II; DADs, delayed afterdepolarizations; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase; ISO, isoproterenol; KI, knockin; RyR2, ryanodine receptor type 2; SCaTs, spontaneous Ca2+ transients; and WT, wild type.
