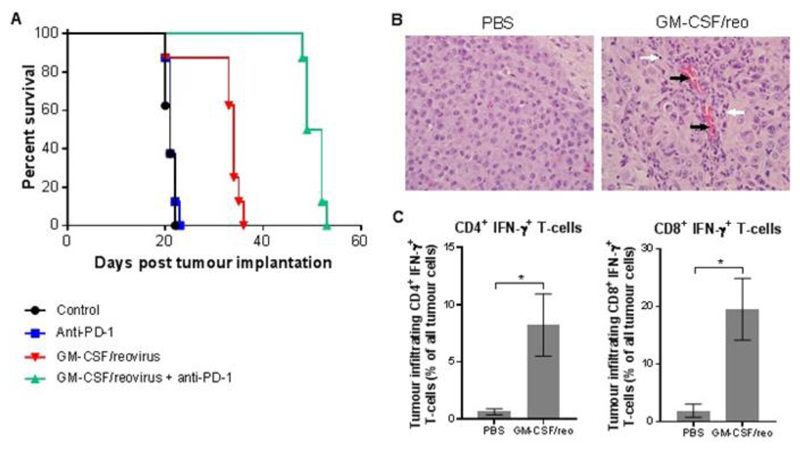
Fig. 5. Combination i.v. reovirus and checkpoint inhibition in an orthotopic syngeneic brain tumor model.
C57/BL6 reovirus-vaccinated mice (22) were injected with GL261 cells intracranially on day one and treated using combinations of GM-CSF plus i.v. reovirus and/or anti-PD-1 antibody. A) Kaplan-Meier survival plot, with Mantel-Cox comparison of survival curves: control vs. Anti-PD-1 P=0.4617, control vs. GM-CSF/reovirus P=0.0012, control vs. GM-CSF/reovirus + anti-PD-1 P<0.0001, GM-CSF/reovirus vs. GM-CSF/reovirus + anti-PD-1 P<0.0001, anti-PD-1 vs. GM-CSF/reovirus + anti-PD-1 P<0.0001. B) Representative brain tumor hematoxylin and eosin stained sections from PBS- and GM-CSF/reovirus treated mice. Black arrows mark vascular endothelial cells; white arrows mark lymphocytes. Scale bars = 30 μm. C) Flow cytometry quantification of CD3+ CD4+ IFN-γ+ or CD3+ CD8+ IFN-γ+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from PBS or GM-CSF/reovirus-treated mice. Graph shows the mean ± SD of four samples.