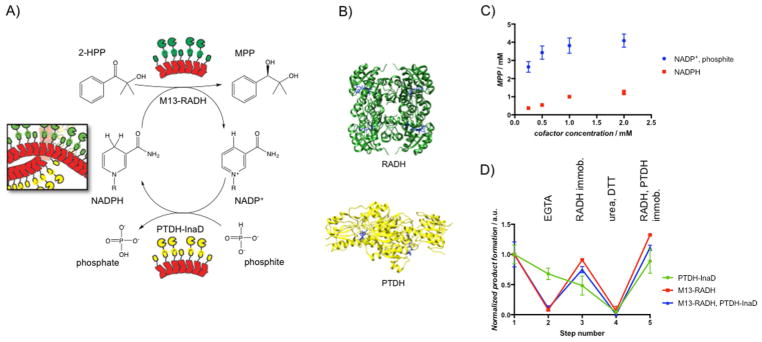
Figure 5.
A) Schematic of the bienzymatic system for stereospecific ketone reduction by using RADH coupled to NADPH cofactor recycling by PTDH. B) Crystal structure of the homotetrameric RADH (PDB: 4BMS) and the homodimeric PTDH (PDB: 4E5N) with NADPH and NAD+ (blue) bound, respectively. C) MPP production as a function of initial concentration of the cofactor. In one case (circles), only NADP+ was supplied, along with 50 mM phosphite. In another case (squares), only NADPH was supplied without phosphite. D) Enzyme activity on a curli fiber mat functionalized with both M13-RADH and PTDH-InaD. The activity of each enzyme was measured individually, independent of the other by controlling the solution and substrate conditions. M13-RADH only (red), PTDH-InaD only (blue), and their combined activity (green) were measured through various steps of removal and re-immobilization and were normalized to their initial activity. Step 1: initial immobilization; step 2: EGTA to remove M13-RADH; step 3: M13-RADH re-immobilization; step 4: 6 M urea and 10 mM DTT to remove all bound enzymes; step 5: re-immobilization of M13-RADH and PTDH-InaD. Points show mean ± standard deviation.