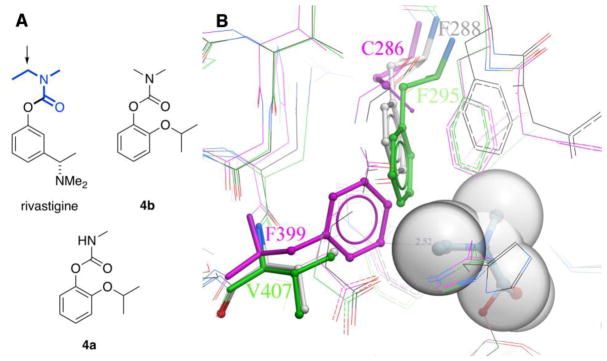
Fig. 2.
A) Comparison of the structures of rivastigmine, dimethylcarbamate 4b, and methylcarbamate 4a. The transferrable ethylmethylcarbamoyl portion of rivastigmine is shown in bold blue; its CH2 unit is indicated with an arrow. B) Overlay of select residues in ethylmethylcarbamoyl T. californica AChE (gray PDB ID: 1GQR), apo hAChE (green, PDB ID: 4EY4, 2.16 Å) and apo G119S AgAChE (magenta, PDB ID: 6ARX, 2.30 Å). The ethylmethylcarbamoyl group of rivastigmine (gray spheres) is covalently attached to the catalytic serine of TcAChE (S200); the phenolic leaving group is not shown. Note that AgAChE residue numberings begin with the start of the conserved catalytic subunit, and do not include the 161-amino acid N-terminal domain. Thus, D1 is D162 in full- length AgAChE, and F399 is F560 in full- length AgAChE.