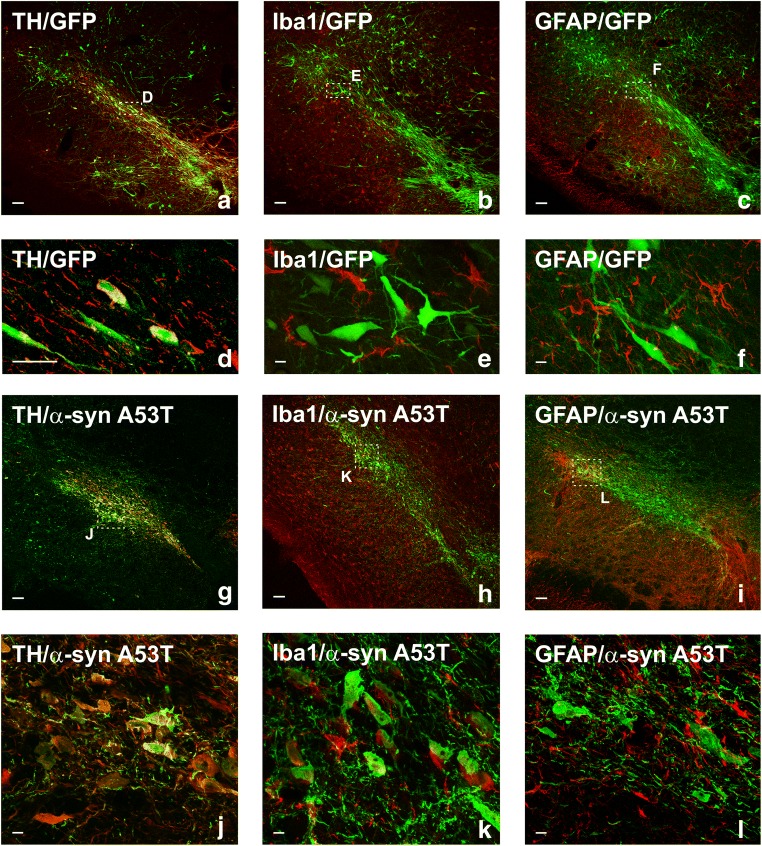
Fig. 1.
Double immunofluorescence for the dopaminergic marker TH (a, d, g, j), or the microglial marker Iba-1 (b, e, h, k), or the astrocytic marker GFAP (c, f, i, l) (red) and different transgenes (GFP: a–f; α-syn-A53T: g–l) in the substantia nigra region 1 week after the injection of AAV9 expressing human GFP or human α-syn-A53T, respectively (green). Laser confocal microscopy shows colocalization (yellow) of GFP or α-syn-A53T with the dopaminergic marker TH (a, d, g, j). However, GFP or α-syn-A53T is not expressed in microglia or astrocytes. Areas squared in (a)–(c) and (g)–(i) are magnified in (d)–(f) and (j)–(l), respectively. Scale bars = 75 μm (a–c, g–i), 25 μm (d), and 7.5 μm (e–f, j–l). Abbreviations: AAV9 = adeno-associated viral vectors serotype 9; α-syn A53T = A53T mutated alpha-synuclein; GFAP = glial fibrillary acidic protein; GFP = green fluorescent protein; Iba-1 = ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1; TH = tyrosine hydroxylase