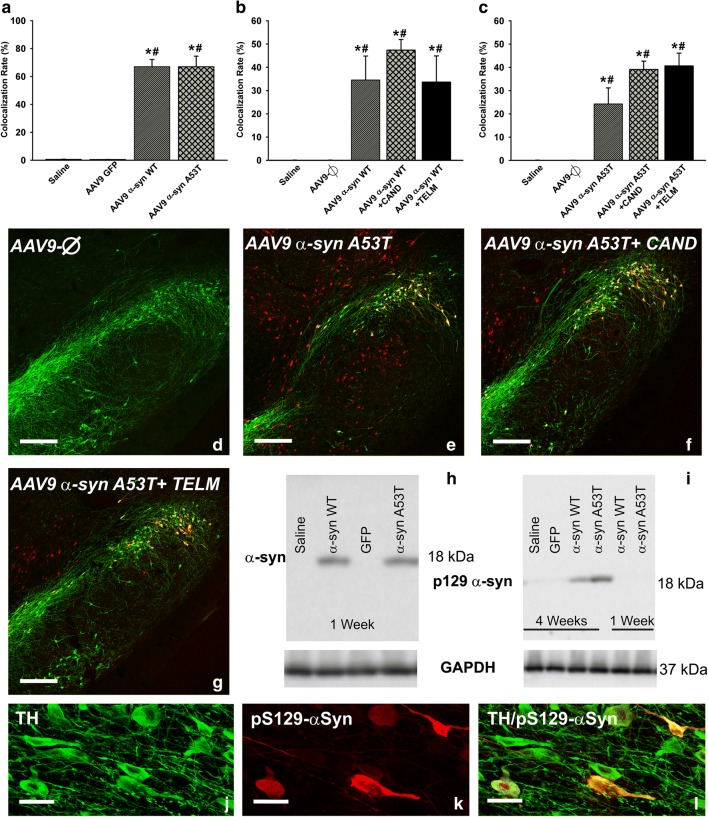
Fig. 3.
Expression of α-syn (a, h) and phosphorylated α-syn (b–g, i–l) 1 week (a, h) and 4 weeks (b–g, i–l) after injection of AAV9 vectors. The rate of expression of α-syn in dopaminergic neurons (TH-ir) of rats injected with AAV9-α-syn WT or AAV9-α-syn A53T is shown in (a). The rate of expression of phosphorylated α-syn in dopaminergic neurons (TH-ir) of rats injected with AAV9-α-syn WT or AAV9-α-syn A53T and treated or not treated with candesartan or telmisartan is shown in (b) and (c). The colocalization (yellow) of phosphorylated α-syn (red) and dopaminergic neurons (green) in the different experimental groups is illustrated in (d)–(g) and magnified in (j)–(l). The expression of α-syn 1 week after injection (h) and phosphorylated α-syn in the nigral region (i.e., dopaminergic and nondopaminergic cells) 1 and 4 weeks after injection (i) was confirmed by Western blot. Data are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 relative to the group injected with saline; #p < 0.05 relative to the AAV9-Ф-injected group. One-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Sidak post hoc test. Scale bars = 250 μm (d–g) and 25 μm (j–l). Abbreviations: α-syn A53T = A53T mutated alpha-synuclein; α-syn WT = wild-type alpha-synuclein; ANOVA = analysis of variance; CAND = candesartan; SEM = standard error of the mean; TELM = telmisartan; Ф = empty-null