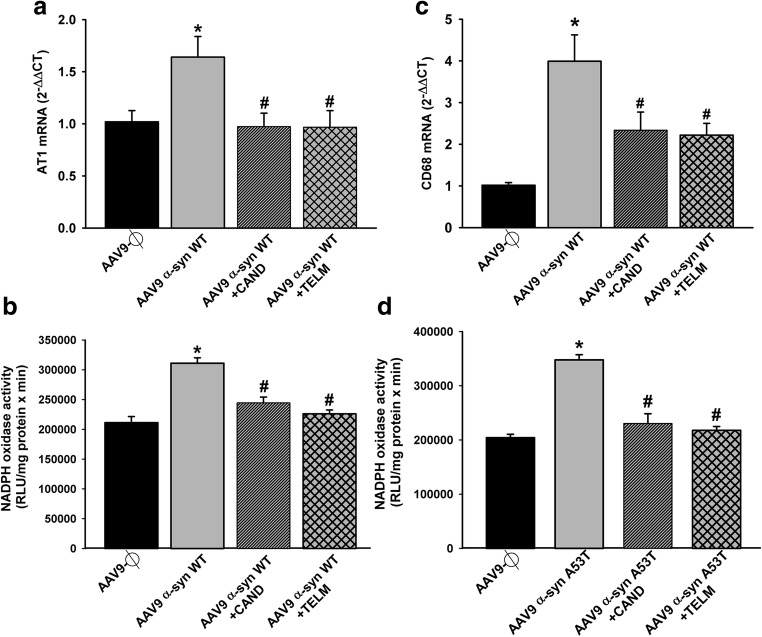
Fig. 9.
Effect of empty AAV9 vectors (AAV9-Ф) or AAV9 expressing human α-syn on the expression of AT1 receptor mRNA, NADPH activity, and markers of phagocytic activity (CD68) in rats not treated or treated with the AT1 antagonist candesartan (CAND) or telmisartan (TELM). AAV9 expressing human WT α-syn induced a significant increase in the expression of AT1 receptor mRNA (a), NADPH activity (b, d), and CD68 (c). A significant increase in NADPH activity induced by AAV9 expressing human A53T α-syn is shown in (d). These changes were inhibited by simultaneous treatment with the AT1 blockers candesartan or telmisartan (a–d). In (a) and (c), the results were normalized to the values of the control group. For RT-PCR, the comparative cycle threshold values method (2−ΔΔCt) was used. Gene expression was measured relative to that of the housekeeping transcripts (β-actin). NADPH oxidase activity was expressed as relative light units (RLU)/min/mg protein). Data are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 relative to the AAV9-Ф-injected group; #p < 0.05 relative to the group injected with AAV9 expressing human α-syn. One-way ANOVA followed by Holm–Sidak post hoc test. Abbreviations: α-syn A53T = A53T mutated alpha-synuclein; α-syn WT = wild-type alpha-synuclein; ANOVA = analysis of variance; AT1 = angiotensin type 1 receptor; CAND = candesartan; CD68 = cluster of differentiation 68; SEM = standard error of the mean; TELM = telmisartan; Ф = empty-null