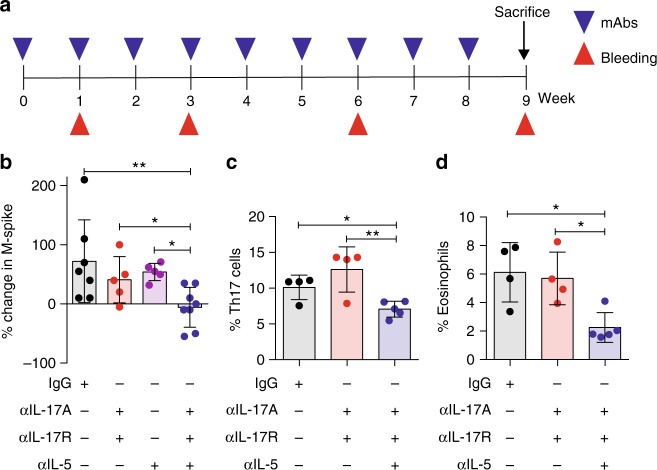
Fig. 6.
IL-17-eosinophil axis neutralization delays disease progression in Vk*MYC mice. a Schematic representation of the experiment. b Percentage change in M-spike in mice within the indicated cohort (Isotype and αIL-17A, αIL-17R, αIL-5: n = 8 mice/group, αIL-17A, αIL-17R and αIL-5: n = 5 mice/group) during the observation period. Frequency of BM Th17 (i.e., CD3+CD4+IL-17+) cells c and eosinophils (i.e., CD11b+Ly6CintMHC-II−Ly6G−SSChi d) was assessed by flow cytometry. Each dot represents an individual mouse. c Mean ± SD of two independent experiment. (Isotype n = 4, αIL-17A, αIL-17R n = 4, αIL-17A, αIL-17R, αIL-5 n = 5). Unpaired t test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. d Mean ± SD of two independent experiment. (Isotype n = 4, αIL-17A, αIL-17R n = 4, αIL-17A, αIL-17R, αIL-5 n = 5). One-way ANOVA P = 0.0101