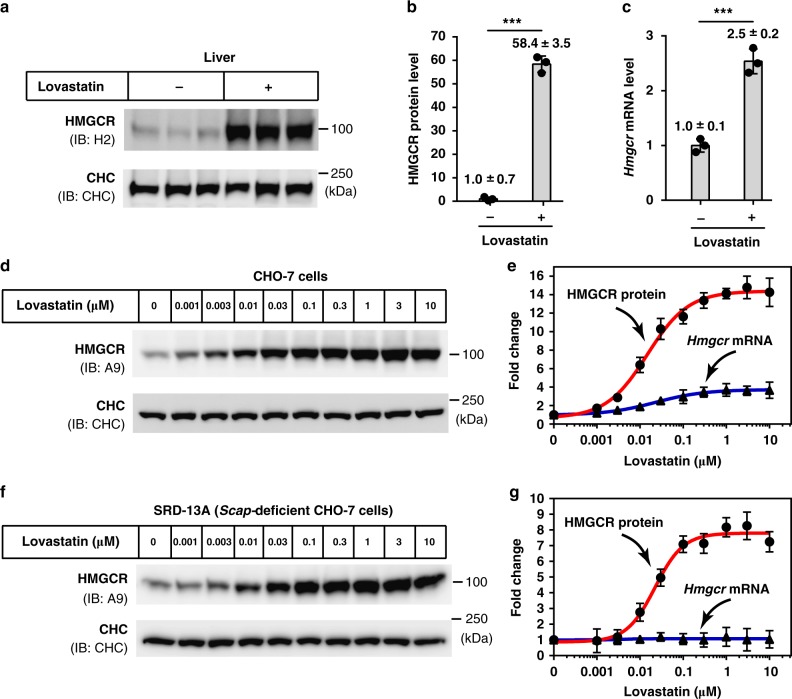
Fig. 1.
Lovastatin causes a substantial accumulation of HMGCR protein. a–c Male C57BL/6J mice (n = 3 per group) were gavaged with vehicle or lovastatin (60 mg/kg/day) once daily for 7 days. Livers were harvested for immunoblotting and RT-qPCR. a Immunoblotting analysis of HMGCR protein from membrane fractions. Clathrin heavy chain (CHC) was a loading control. b Quantifications of HMGCR protein shown in a. The HMGCR protein level of mice gavaged with vehicle was defined as 1. c Quantifications of Hmgcr mRNA level by RT-qPCR. The Hmgcr mRNA level of vehicle-treated mice was defined as 1. Cyclophilin was used as the reference gene. d, e CHO-7 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of lovastatin for 16 h, then harvested for immunoblotting and RT-qPCR. d Immunoblotting analysis of HMGCR protein. e Dose–response curves of HMGCR protein and Hmgcr mRNA levels. HMGCR protein and Hmgcr mRNA levels of DMSO-treated cells were defined as 1. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) was a reference gene. f, g SRD-13A cells were treated with lovastatin for 16 h. f HMGCR protein was analyzed by immunoblotting. g Hmgcr mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR. Data are from three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Source data are provided as a Source Data File. Uncropped immunoblots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9