Figure 5.
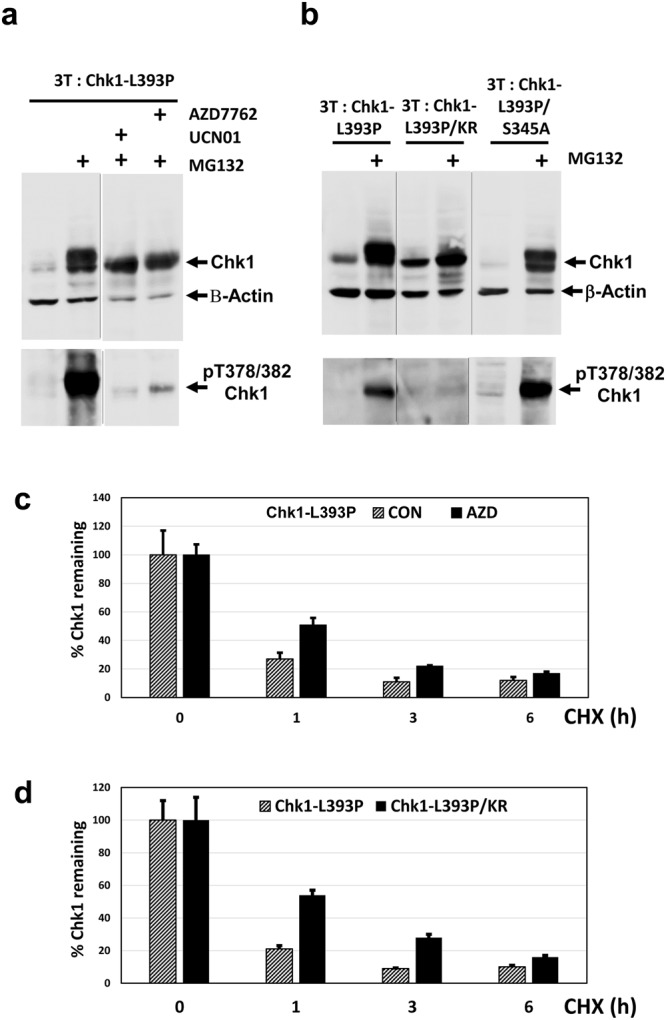
Chk1 378/382 auto-phosphorylation accelerates proteasomal degradation. (a) 3T: Chk1-L393P DT40 cells were treated with DOX for 16 hours in the presence or absence of MG132 plus or minus the Chk1 inhibitors UCN01 and AZD7762. Cell extracts were prepared, 30 μg resolved by SDS-PAGE, and analysed by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Upper and lower panels are derived from the same western blots (see Supplementary Information for original images). (b) The indicated DT40 cell lines were treated with DOX for 16 hours plus or minus MG132 to induce the expression of Chk1-L393P, and the Chk1-L393P/KR and Chk1-L393P/S345A double mutant proteins (see text for additional explanation) under conditions where the proteasome is active or inhibited. Cell extracts were prepared, 30 μg resolved by SDS-PAGE, and analysed by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Samples in the upper and lower panels respectively are derived from two western blots run, processed and imaged in parallel in each case (see Supplementary Information for original images). (c) Chk1-L393P protein expression was induced by treatment with DOX for 16 hours followed by further treatment with cycloheximide (CHX) for 1, 3, and 6 hours to block protein synthesis in the presence or absence of the Chk1 inhibitor AZD7762. Cell extracts were prepared, 30 μg resolved by SDS-PAGE in triplicate, and analysed by western blotting using antibodies recognising total Chk1 and β-Actin. Shown is the mean and standard deviation of three independent determinations of the amount of Chk1 remaining for each treatment using β-Actin to correct for loading. Control values at t = 0 have been converted to 100% to facilitate comparison of relative protein stability under each condition. (d) Chk1-L393P and Chk1-L393P/KR protein expression was induced by treatment with DOX for 16 hours followed by further treatment with cycloheximide (CHX) for 1, 3, and 6 hours to block protein synthesis. Cell extracts were prepared, 30 μg resolved by SDS-PAGE in triplicate, and analysed by western blotting using antibodies recognising total Chk1 and β-Actin. Shown is the mean and standard deviation of three independent determinations of the amount of Chk1 remaining for each treatment using β-Actin to correct for loading. Control values at t = 0 have been converted to 100% to facilitate comparison of relative protein stability.
