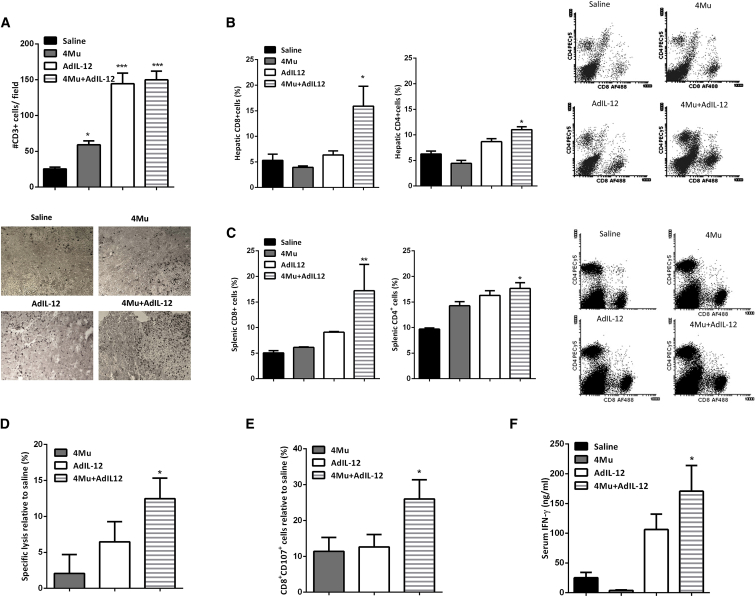
Figure 2.
Combined Therapy Promotes Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells and Induces a Potent Cytotoxic-Specific T Cell Response
(A) Combined therapy showed higher levels of tumor-infiltrating CD3+ T cells. *p < 0.05, saline versus 4Mu; ***p < 0.001, saline versus 4Mu+AdIL-12; and ***p < 0.001, saline versus AdIL2, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (B) Percentage of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in liver tissue. *p < 0.05, saline versus 4Mu+AdIL12; one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Levels of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells of total live cells in spleen of mice. *p < 0.05, saline versus 4Mu+AdIL-12; **p < 0.01, saline versus 4Mu+AdIL-12, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Splenocytes derived from 4Mu+AdIL12-treated mice exerted a potent CTL activity relative to that of the saline group against Hepa 129 cells, determined by LDH release. *p < 0.05, 4Mu+AdIL12, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (E) Splenocytes derived from 4Mu+AdIL12-treated mice exerted a potent CTL activity relative to that of the saline group against Hepa 129 cells, determined by CD107 expression. *p < 0.05 for 4Mu+AdIL12, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (F) Quantification of serum interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels by ELISA; mice treated with combined therapy showed higher levels of IFN-γ; *p < 0.05 for saline versus 4Mu+AdIL12, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM.