FIGURE 1.
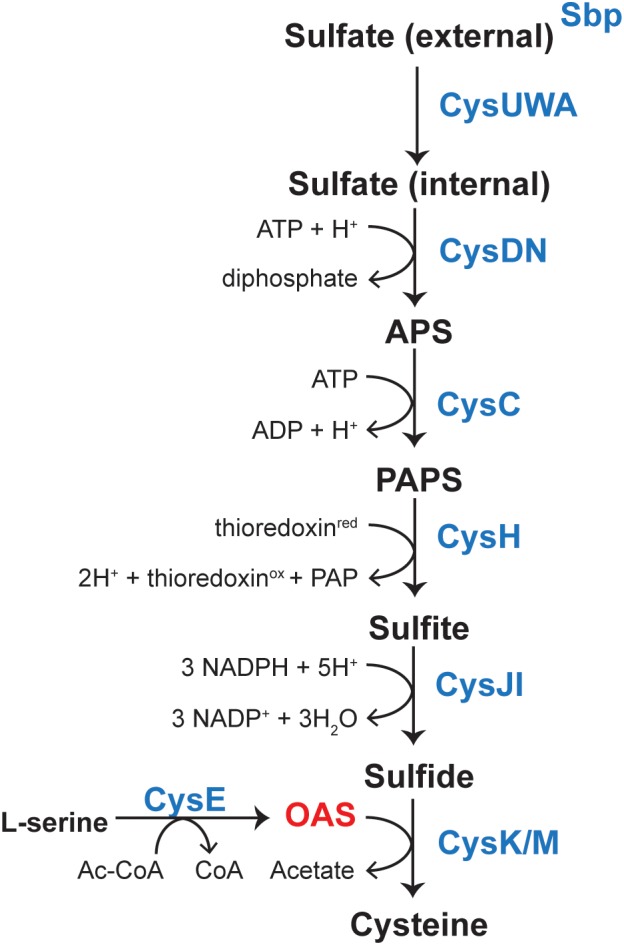
Pathway for biosynthesis of L-Cys in Salmonella enterica. Sulfate is sequestered by the sulfate-binding protein (sbp) and uptake is mediated by the CysUWA sulfate/thiosulfate transporter. The ATP sulfurylase [CysD (catalytic subunit)/CysN (GTP-binding subunit), EC 2.7.7.4] activates sulfate to adenosine 5′-phosphate (APS), which is a substrate for APS kinase (CysC, EC 2.7.1.25). 3-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (PAPS) is reduced to sulfite by the PAPS reductase (CysH, EC 1.8.4.8) and sulfite is reduced to sulfide by a NADPH-sulfite reductase (CysJI, EC 1.8.1.2). A serine acetyltransferase (CysE, EC 2.3.1.30) produces OAS from L-Ser and AcCoA. OAS and sulfide are then substrates for cysteine synthase (CysK, EC 2.5.1.47), which produces L-Cys. Transcription of cysJIH and cysK is upregulated upon binding of CysB and acetyl-serine.
