Figure 1.
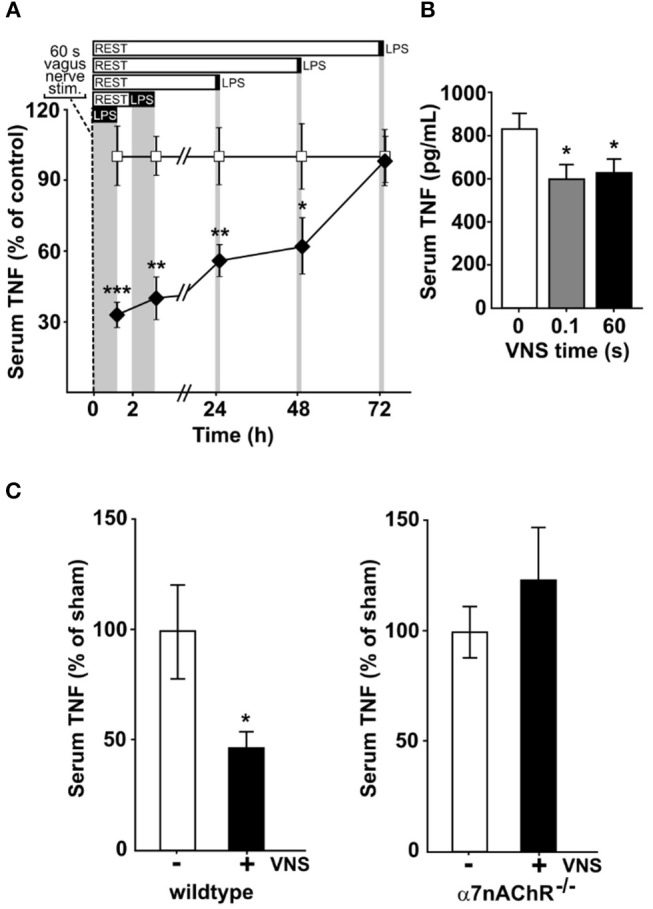
Vagus nerve stimulation suppresses endotoxin-induced serum TNF levels for days. Animals were subjected to vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) at 10 Hz followed by intraperitoneal endotoxin (LPS) injection at a specified time after VNS and then euthanized 90 min after endotoxin administration. Serum was collected and analyzed for TNF by ELISA. (A) Rats (n = 4–13/group) were subjected to 60 s of VNS or sham surgery. Open squares: mean TNF ± SEM in sham animals, filled diamonds: mean TNF ± SEM in vagus nerve stimulated animals. (B) Mice were subjected to 0 (n = 9), 0.1 s (n = 7), or 60 s (n = 9) of VNS and rested for 24 h before endotoxin injection. Means ± SEM are plotted. (C) Wild type (n = 7; left) and α7nAChR−/− (n = 7; right) male mice were subjected to 60 s of VNS or sham surgery and rested for 24 h before endotoxin injection. TNF levels relative to unstimulated animals are shown as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
