Figure 2.
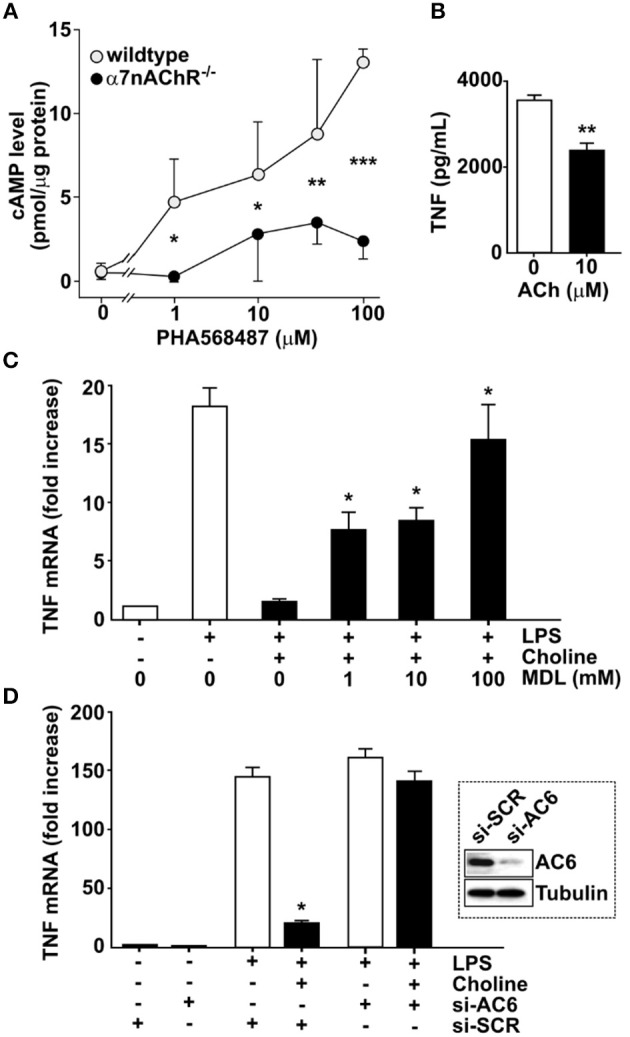
Adenylyl cyclase 6 mediates inhibition of TNF. (A) Bone-marrow derived macrophages from wild type (n = 2) and α7nAChR −/− (n = 3) mice were exposed to the α7nAChR selective agonist PHA568487 and cAMP analyzed in the cell lysate. Results are shown as mean cAMP levels normalized to protein concentration (pmol/μg) ± SEM. Open circles—wild type, filled circles—α7nAChR −/− cells. (B) RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cells were incubated with 10 μM acetylcholine for 1 h. The ACh was removed and 24 h post ACh, the cells were exposed to endotoxin (LPS) for 4 h. TNF was measured in the culture medium using ELISA. Plotted values are mean ± SEM. (C) RAW 264.7 cells were incubated with the adenylyl cyclase inhibitor MDL 12,330A, then exposed to choline and endotoxin. Values shown are mean fold increase of endotoxin-induced TNF mRNA ± SEM relative to cells exposed to endotoxin and choline in the absence of MDL 12,330A. (D) Adenylyl cyclase 6 (AC6) was knocked down using siRNA in RAW 264.7 cells which were then exposed to the α7nAChR selective agonist choline. Western blot shows AC6 in cells treated with siRNA targeting AC6 (si-AC6) or scrambled siRNA (si-SCR). Bars represent fold increase ± SEM of TNF mRNA compared to cells not challenged with endotoxin. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
