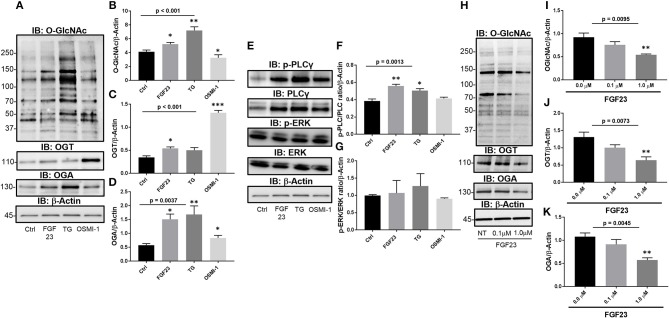
Figure 1.
FGF23 stimulates the HBP/O-GlcNAc modification of proteins via the PLCγ signaling pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells. (A) Representative Immunoblots showing global O-GlcNAc, OGT, OGA, and β-Actin from HBECs treated as described. (B–D) Densitrometric quantitation of O-GlcNAc, OGT, and OGA from (A). (E) Representative Immunoblots showing phosphorylation of PLCγ and ERK, total PLCγ and ERK, and β-Actin from HBECs treated as described. (F,G) Densitrometric quantitation of Immunoblots from (A). (H) Representative Immunoblots of global O-GlcNAc, OGT, OGA, and β-Actin from HBECs treated with a PLCγ inhibitor (U73122 at 0, 0.1, and 1.0 μM) and FGF23 (20 ng/ml) for 24 h. (I–K) Densitrometric quantitation of O-GlcNAc, OGT, and OGA from (H). Western blots were performed as triplicates of the same experiment. Statistical analysis was done using ANOVA or Student's t-test showing means ± S.E.M. with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. Ctrl, Control; FGF23, fibroblast growth factor 23; TG, thiamet G (OGA inhibitor); OSMI-1, OGT inhibitor.