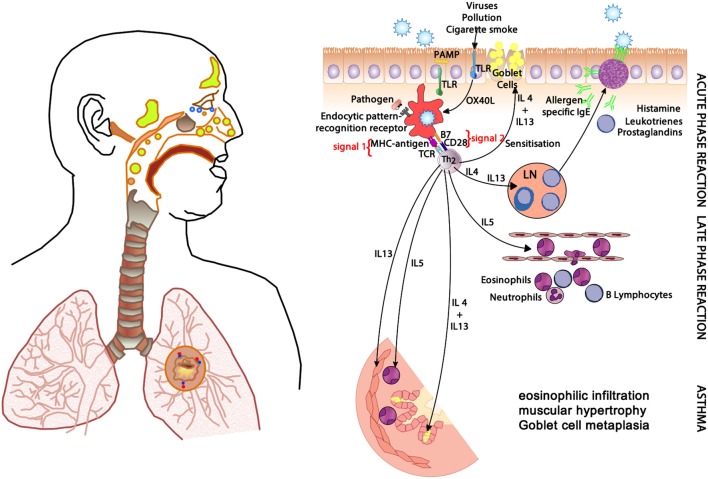
Figure 5.
The clinical changes and physiological mechanisms of allergic respiratory disease. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) present allergen-derived peptides lodged within the MHC molecule to T cells within a TH2 milieu, resulting in allergy mediated by eosinophils and IgE derived from plasma cells (transformed from activated B cells). PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; TLR, toll-like receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T cell receptor; IgE, immunoglobulin E; OX40L, CD252; B7, CD28; IL-4, interleukin-4; IL-5, interleukin-5; IL-13, interleukin-13.