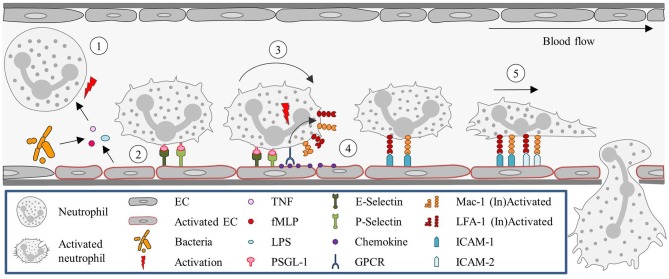
Figure 1.
Neutrophil recruitment in the post-capillary venules of the cremaster muscle. (1) Neutrophils are primed upon exposure to inflammatory agents, such as cytokines (e.g., TNF) and DAMPs (fMLP) or PAMPs (LPS), in the context of sterile or non-sterile inflammation, respectively, or interaction with activated ECs. (2) Neutrophil capture is mediated by P- and E- selectin, (3) followed by rolling, which is also largely regulated via selectin signaling. (4) Subsequently, neutrophils firmly adhere to ECs. This step is dependent on integrin (LFA-1 and Mac-1) activation, which is mediated by GPCRs interacting with chemokines presented on the endothelium. (5) Neutrophils then crawl along the endothelium, via ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 interactions with Mac-1 and LFA-1, until they reach their site of TEM. EC, Endothelial cell; fMLP, N-formyl peptides; GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor; ICAM, Intracellular adhesion molecule; LFA-1, Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; Mac-1, Macrophage-1 antigen; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; TEM, Transendothelial migration; TNF, Tumor-necrosis factor.