Figure 4.
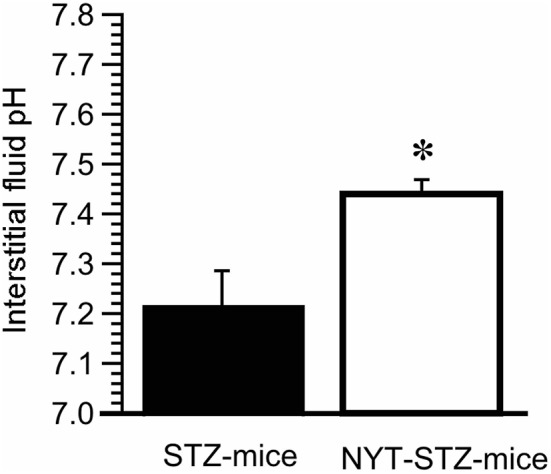
Effects of Ninjin'yoeito (NYT) on the interstitial fluid pH around the gastrocnemius muscle of STZ-mice. The pH measurement was performed just after obtaining the blood sample to determine the casual serum glucose level without any forced fasting 14 days after starting the NYT intake. The interstitial fluid pH around the gastrocnemius muscle was lower in STZ-mice (pH = 7.22 ± 0.07; n = 6) compared with that in “non-STZ-injected non-diabetic” mice (pH = 7.40 ± 0.03; n = 6; p < 0.05). On the other hand, NYT significantly improved the interstitial fluid pH around the gastrocnemius muscle from pH = 7.22 ± 0.07 (the closed column; n = 6) to pH = 7.44 ± 0.03 (the open column; n = 6; p < 0.05), which was identical to that in “non-diabetic” control mice (pH = 7.40 ± 0.03; n = 6). *p < 0.05, vs. NYT-untreated STZ-mice group (STZ-mice; the closed column). Each group represents the mean ± SEM of 6 mice.
