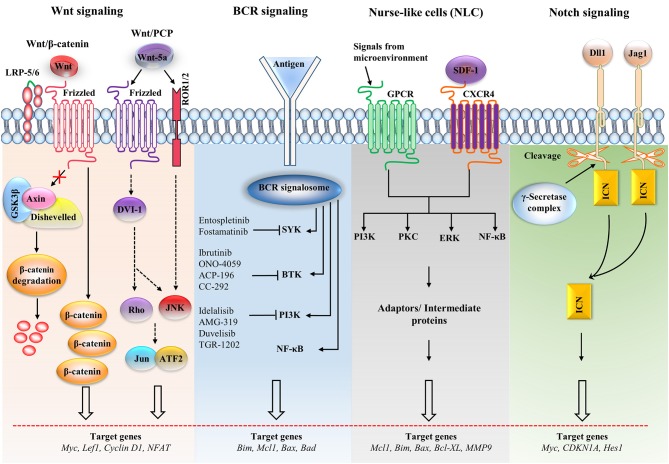
Figure 2.
Major signaling pathways and therapeutic targets in CLL cells. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is activated by the Wnt ligand attached to Frizzled and LRP-5/6 receptors that activate disheveled (dsh), resulting in the inactivation of the destruction complex. This inactivation causes the accumulation of β-catenin, which enters the nucleus. The nuclear translocation of β-catenin allows it to interact with the transcription factor TCF/LEF and induces the transcription of the target genes. The non-canonical Wnt pathway [Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP)] is triggered by Wnt-5a that enhances the heterodimerization of receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) and ROR2. Receptor binding leads to the formation of the ligand-receptor complex and downstream activation of the dsh protein (DVI-l), Rho GTPases and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which together regulate tissue polarity and cell motility, and has also been implicated in organogenesis and cancer metastasis. B cell receptor (BCR) signaling causes a signalosome containing spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK), Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), and adaptor proteins to form, which activates downstream pathways. Small molecule inhibitors are shown in the BCR pathway. In nurse-like cells (NLCs), the interaction of chemokines with receptors generates microenvironmental signaling. NLCs regulates several signaling pathways, including the protein kinase C (PKC), PI3K, extracellular regulated kinase (ERK), and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways, which are similar to the BCR pathway. In the Notch signaling pathway, the ligands [Dll1, Jagged-1 (JAG1)] bind with the receptor and cause the intracellular Notch domain (ICN) to be cleaved by the g-secretase complex. The cleaved domain then translocates to the nucleus, forms complex with other proteins and activates target genes. BAD, Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death; Bcl-XL, B-cell lymphoma-extra-large; CDKN1A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; GPCR, G-protein coupled receptor; LEF1, Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1; LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1.