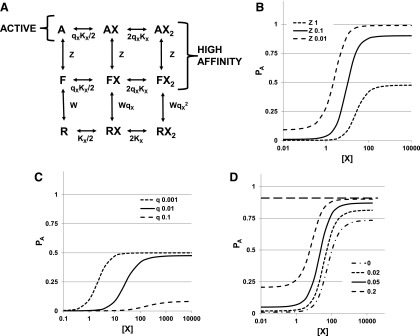
Fig. 5.
An extension of the MWC model incorporating a high-affinity closed state. (A) A kinetic scheme incorporating a state with high affinity for agonist for a resting receptor. In addition to the R state (low affinity, resting) and A state (high affinity, active), the receptor can adopt an F state (high affinity, resting). In the absence of agonist, W = R/F and Z = F/A. KX is the affinity of the R state for X (KX,R) and qX is the ratio of the affinity of the flipped or active states to that of the closed state (qX = KX,A/KX,R). Note that Z does not change with binding of X to the receptor. (B and C) Activation curves for combinations of parameters; in (B), the effects of altered values for Z are shown, whereas q is changed in (C). [In both (B and C), W = 1000, KX = 100, and NX = 2; in (B), qX = 0.01, whereas Z is changed from 0.01 to 1, as indicated, and in (C), Z = 1 whereas qX = is changed from 0.001 to 0.1]. (D) The interaction between two drugs acting at different sites. The activation curve for drug X is shown in the absence of Y and in the presence of Y at concentrations eliciting responses with PA of 0.02, 0.05, and 0.2 as indicated (W = 1000, Z = 0.1, NX = 2, KX = 100, qX = 0.05, NY = 2, KY = 100, qY = 0.05).