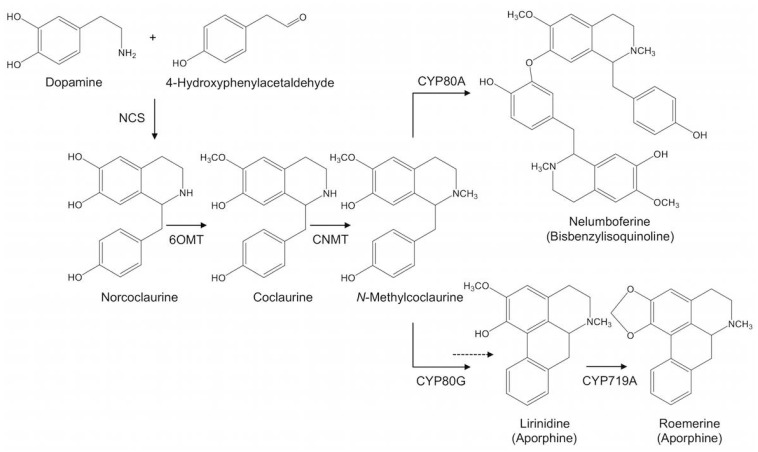
Figure 5.
Suggested BIA biosynthetic pathway in sacred lotus. The scheme shows norcoclaurine as the common precursor and N-methylcoclaurine as the branch point intermediate in the formation of aporphine and bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Tailoring reactions, such as O- and N-methylations, hydroxylation, oxidation, C-C and C-O coupling (and a possible dehydration represented by the dashed arrow) yield the diverse BIAs reported in Nelumbo nucifera. Note that other 1-benzylisoquinolines derived from norcoclaurine could be used in the formation of aporphine and bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids, as this representation is merely one of many possible routes (e.g., major BIAs in sacred lotus such as nuciferine and neferine are not represented). Stereochemistry has been omitted for simplicity. Abbreviations: 6OMT, norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase; CNMT, coclaurine N-methyltransferase; CYP719A, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase 719A, CYP80A, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase 80A; CYP80G: cytochrome P450 monooxygenase 80G; NCS, norcoclaurine synthase.