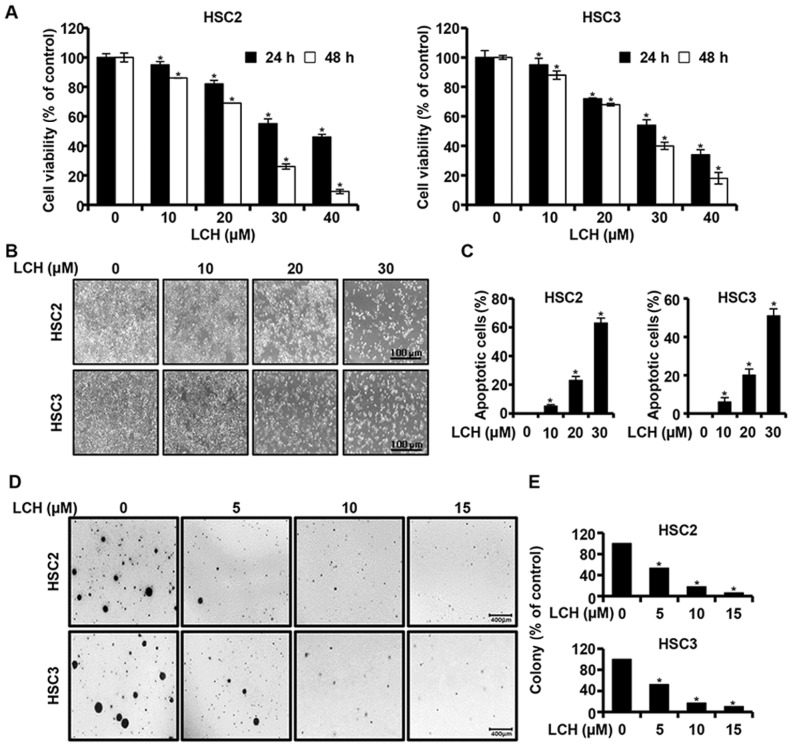
Figure 1.
Anticancer effect of LCH on OSCC. (A) Viabilities of HSC2 and HSC3 OSCC lines treated with LCH (0–40 µM) for 24 and 48 h. Viability was measured using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxy-methoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium assay kit. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. (B) Following treatment with LCH for 48 h, morphological changes in OSCC cells were detected using an optical microscope. (C) Cell nuclei were stained with 4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole and images were captured with a fluorescence microscope. DNA fragmentation and nuclear condensation were quantified, and the data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3; *P<0.05). (D) HSC2 and HSC3 cells were treated with LCH (5, 10 and 15 µM) in 1 ml of 0.3% basal medium Eagle's agar containing 10% fetal bovine serum. All cells were incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator for 20 days and colonies were counted. (E) Numbers of colonies were calculated as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3; *P<0.05). OSCC, oral squamous cell carcinoma; LCH, licochalcone H.