FIGURE 10.
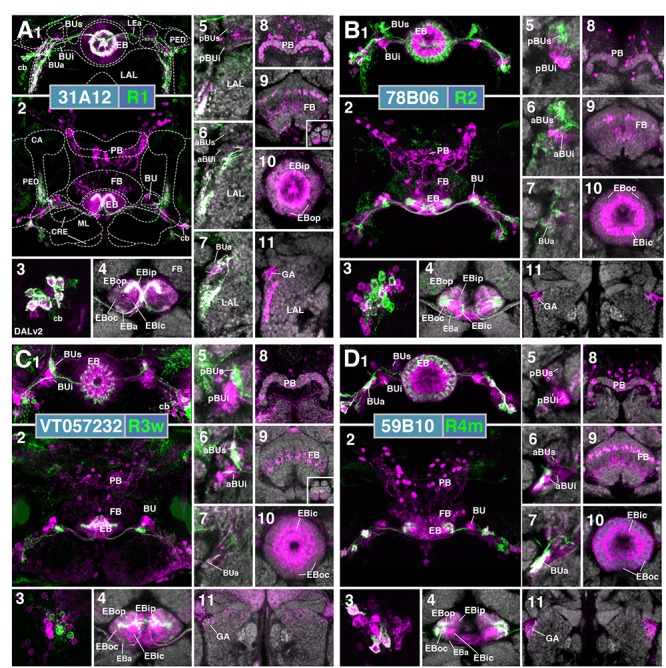
Putative postsynaptic partners of R-neurons revealed by trans-Tango. (A–D) Confocal z-projections of Gal4 drivers that label distinct R-neuron subclasses in conjunction with trans-Tango mediated labeling of postsynaptic neurons. Each lettered, 11-paneled module corresponds to an individual driver. Gal4-expressing R-neurons labeled by GFP under UAS control (green) and putative postsynaptic neurons are labeled by RFP under trans-Tango mediated QUAS control (magenta). Larger white annotations denote arborization-containing domains of interest; smaller white annotations represent spatial landmarks. Module organization outlined below: (1) Frontal z-projection spanning from R-neuron cell bodies to the ellipsoid body (EB)/bulbs (BU). (2) Z-projection from the dorsal view spanning the antero-posterior depth of the brain (anterior pointing downward). (3) Image of DALv2 R-neuron cell bodies (cb) to illustrate degree of colocalization between pre- and post-synaptic neurons, an indication of homotypic interactions within a cell type. (4–11) Neuropil is labeled with anti-DN-cadherin (gray). (4) Horizontal section of the EB spanning the length of the EB canal. (5–7) Frontal sections of the bulb at three different depths. From top to bottom: (5) posterior section containing the posterior regions of the superior (pBUs) and inferior (pBUi) bulb, (6) intermediate section containing the anterior regions of the superior (aBUs) and inferior (aBUi) bulb, (7) anterior section containing the anterior (BUa) bulb. (8–11) Isolated postsynaptic targets (shown in magenta) throughout the CX (Gal4-expressing neurons are shown not shown). Four frontal sections of the CX and its associated neuropils; from top (posterior-most) to bottom (anterior-most): (8) PB, (9) FB and noduli (NO) in inset when applicable, (10) EB, (11) gall (GA)/lateral accessory lobe (LAL). (A1–11) (R1) R31A12-Gal4 > trans-Tango. (B1–11) (R2) R78B06-Gal4 > trans-Tango. (C1–11) (R3w) VT057232-Gal4 > trans-Tango. (D1–11) (R4m) R59B10-Gal4 > trans-Tango. CRE, crepine; ML, PED, and CA, medial lobe, peduncle, and calyx of the mushroom body, respectively; LEa, anterior component of the lateral ellipsoid fascicle.
