FIGURE 5.
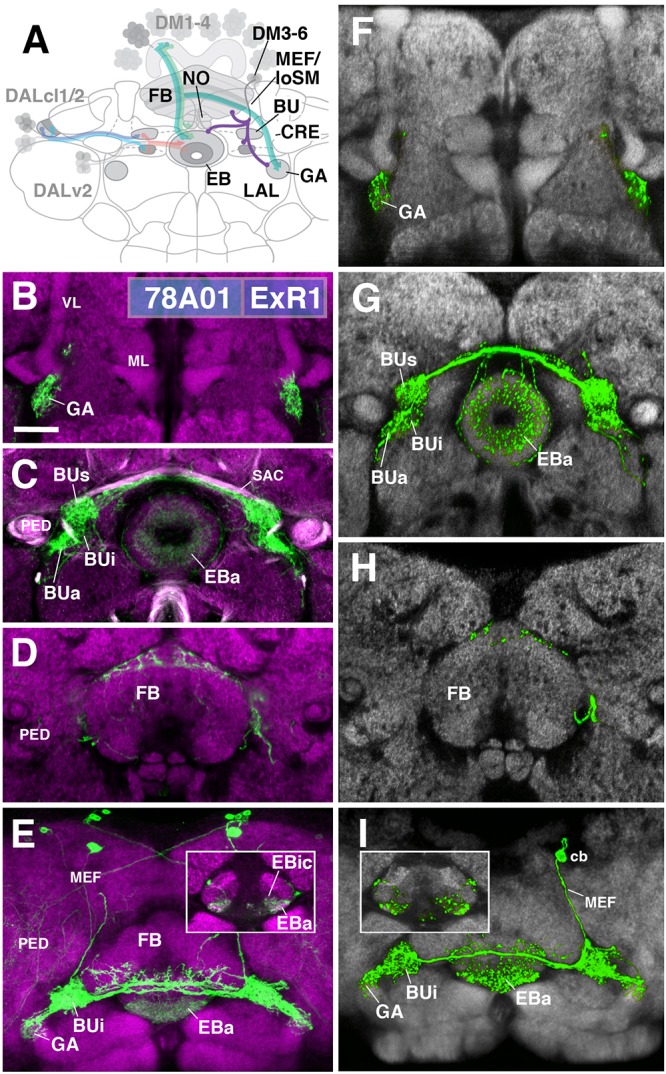
ExR1-neurons: posterior extrinsic ring neurons of lineages CM4, CM3, CM1/DM4-6. (A) Schematized overview of interacting neuronal populations of the EB from Figure 1, now including posterior ExR-neuron subclasses of lineages CM4, CM3, CM1, DPMpm2/DM3-6 (refers also to Figures 6, 7). (B–E) Confocal z-projections of R78A01-Gal4 driver that labels ExR1-neurons. Neurons labeled with 10xUAS-mCD8::GFP (green). Neuropil labeled by anti-DN-cadherin (magenta). Top three rows correspond to frontal sections at three different antero-posterior depths; from top to bottom: anterior section containing the gall (GA)/LAL, intermediate section containing the EB and bulbs (BU), posterior section containing the FB and noduli (NO). Bottom (fourth) row is a horizontal section visualizing the length of the EB canal. Larger white annotations denote arborization-containing domains of interest; smaller white annotations represent spatial landmarks. Inset in panel (E) depicts dorsal view of the EB; R78A01-Gal4 innervates EBa and the anterior part of EBic. (F–I) Confocal z-projections of individually labeled cells generated by MCFO using 78A01-Gal4. Four panels depict the same sections and are organized in the same fashion as in panels B–E. Neuropil labeled by anti-DN-cadherin (gray). Much like the R78A01-positive population, an individual ExR1 neuron innervates (F) the GA and (G) all BU partitions on both sides, along with EBa. (H) Additional innervation includes the dorsal roof of the FB. (I) Dorsal view illustrates that the cell body (cb) of an individual cell, located in the posterior cortex, sends a projection along the medial equatorial fascicle (MEF) and arborizes in both EBa and EBic (inset). CRE, crepine; loSM, longitudinal superior medial fascicle; ML, medial lobe; VL, vertical lobe; PED, peduncle of the mushroom body; SAC, superior arch commissure. Scale bars represent 25 μm (B–I).
