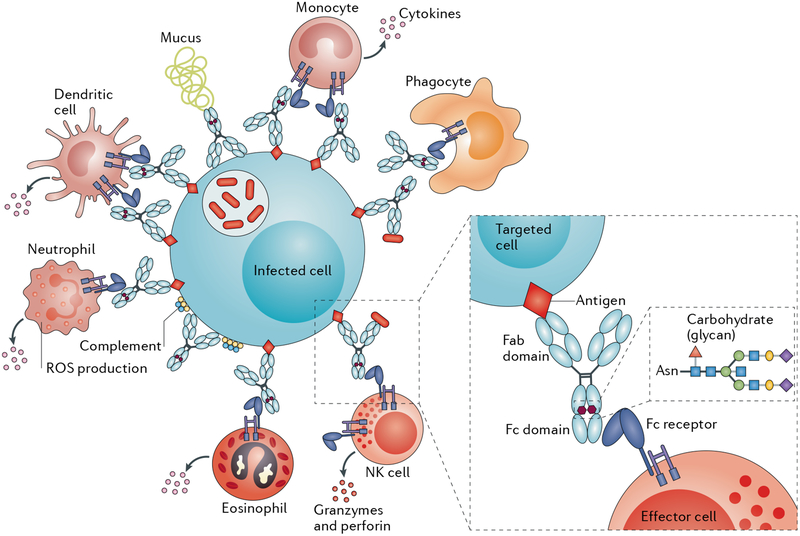
Fig. 4 |. Antibody-mediated resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Beyond their role in clearing pathogens, antibodies also direct the rapid destruction of infected cells via the recruitment of innate immune cells (such as phagocytes) that express crystallizable fragment (Fc) receptors. Two modifications to the Fc domain of an antibody control its affinity for Fc receptors, namely, changes in the antibody subclass or isotype and its glycosylation. Fab, antigen-binding fragment; NK cell, natural killer cell; ROS, reactive oxygen species.