Fig. 1.
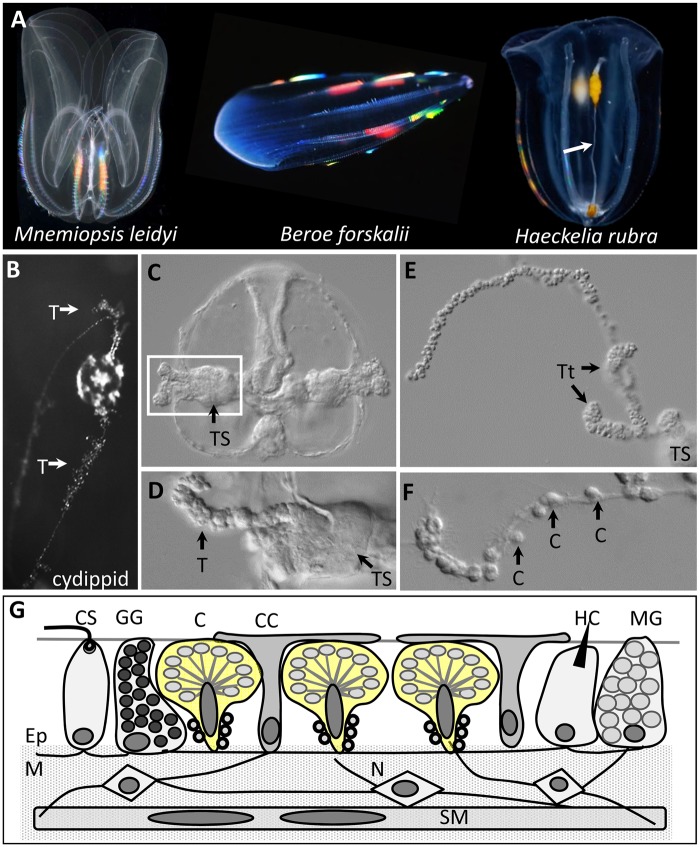
Tentacle morphology varies across ctenophores. (A) Mnemiopsis leidyi has reduced tentacles as an adult, Beroe forskalii lacks tentacles completely, and Haeckelia rubra has long unbranched tentacles (white arrow). (B) The cydippid (larval) stage of M. leidyi has long branched tentacles (T). (C) DIC micrograph of a cydippid with tentacles retracted into the tentacle sheath (TS). (D) Higher magnification of the boxed area in C showing a branched tentacle (T) emerging from the tentacle sheath. (E) Emerging tentacle showing partially contracted side branches (tentilla, Tt). (F) Fully extended tentacle showing colloblast islets (C) along the tentacle. (G) Tentacle cell types—neurons (N) and smooth muscle cells (SM) are in the mesogleal core (M); colloblasts (C; yellow), covering cells (CC), ciliated sensory cells (CS), granular gland cells (GG), hoplocytes (HC), and mucous gland cells (MG) are in the epidermis (Ep). Images in panel A courtesy of Bruno Vellutini (M. leidyi) and Steve Haddock (B. forskalii, and H. rubra).