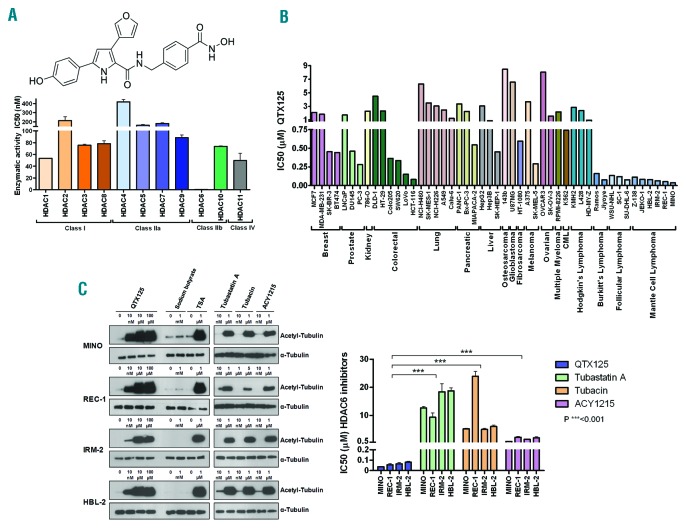
Figure 1.
Chemical structure and HDAC specificity of QTX125 and its effect on α-tubulin acetylation and cell growth. (A) (Top) Chemical structure of QTX125. (Below) In vitro enzymatic activity of 11 HDACs upon QTX125 use. (B) Growth-inhibitory effect of QTX125 in cancer cell lines determined by the MTS assay. (C) (Left) Western-blot assays in MINO, REC-1, IRM-2 and HBL-2 cells show the induction of α-tubulin hyperacetylation upon QTX125 administration. Sodium butyrate is shown as an HDAC inhibitor that does not affect HDAC6 (negative control). TSA is shown as an HDAC inhibitor that affects all HDAC classes, including HDAC6 (positive control). The effect of the three available specific HDAC6 inhibitors (tubastatin A, tubacin, and ACY1215) is also shown. Total α-tubulin is used as a loading control. (Right) Growth-inhibitory effect of QTX125 in the mantle cell lymphoma cell lines determined by the MTS assay in comparison to the other, previously described HDAC6 inhibitors. CML: chronic myelogenous leukemia.