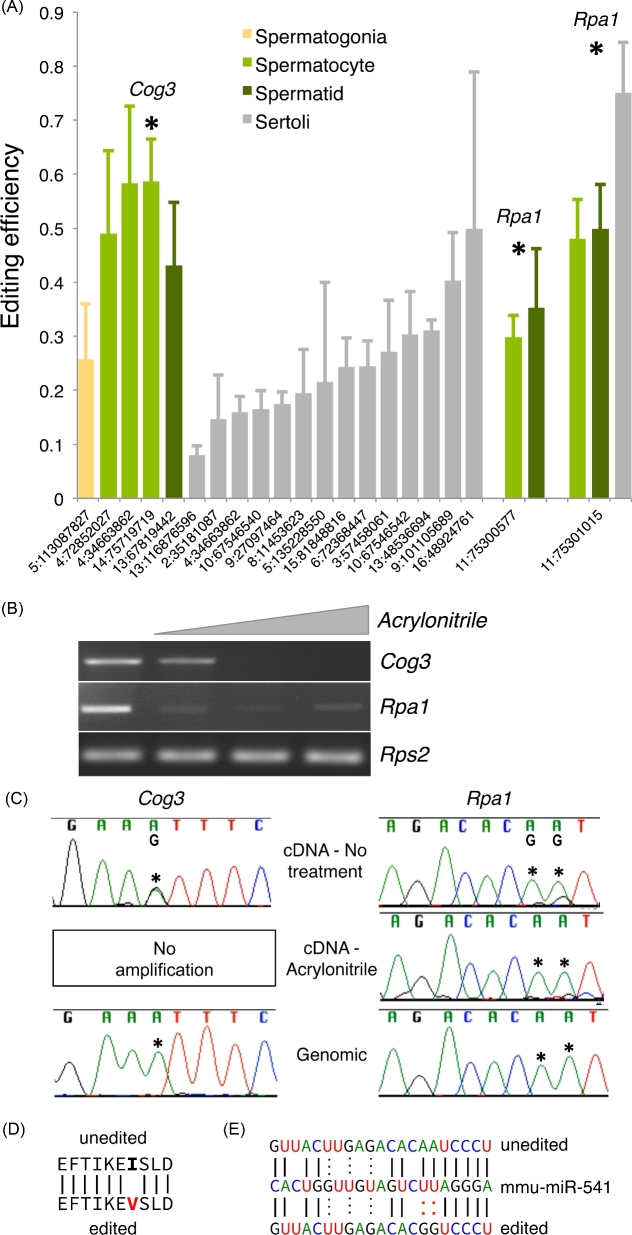
Figure 1.
RNA editing is rare and cell-type dependent in the testis. (A) Editing efficiency of computationally identified A-to-I RNA-editing sites in RNA-sequencing data of isolated testicular cell populations (n = 3). X-axis coordinates—editing site location within the genome. Asterisks—sites also identified in whole testis RNA-sequencing data (n = 6), host genes selected for further study indicated above respective editing sites. Error—standard deviation. (B) Molecular confirmation of inosine incorporation by acrylonitrile treatment. (C) Sanger sequencing of untreated cDNA, acrylonitrile treated cDNA, and genomic DNA to confirm editing, inosine incorporation, and genotype. Asterisks—editing sites. Impact of editing event on the (D) coding potential of Cog3 and (E) a microRNA recognition site in the 3΄ UTR of Rpa1.