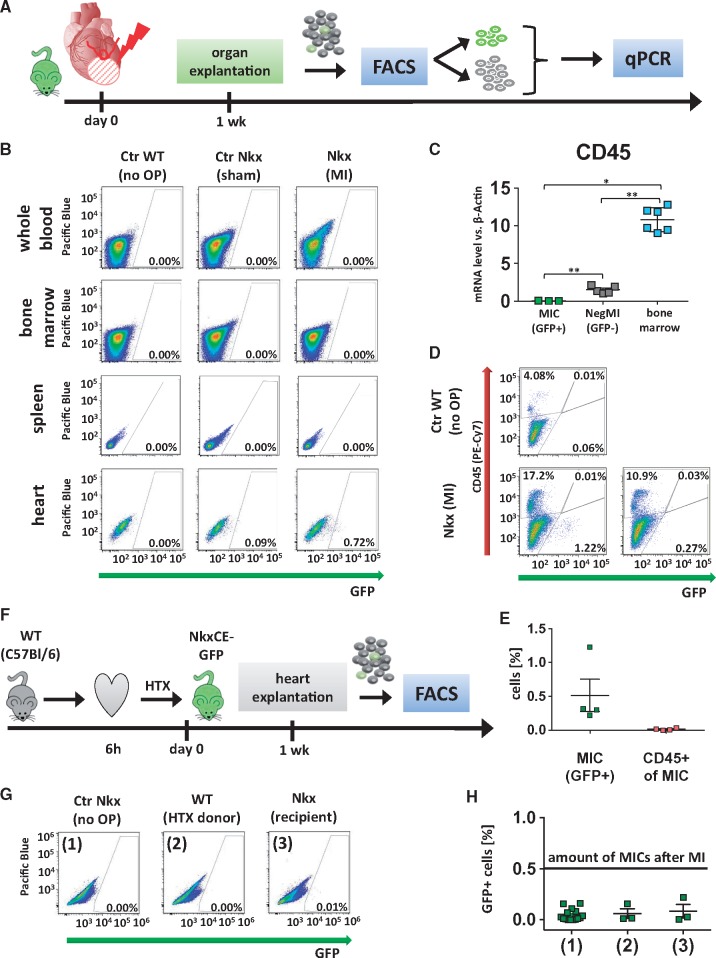
Figure 3.
Origin of NkxCE-GFP+ MICs. (A) One week after MI was induced in NkxCE-GFP mice (n = 4), hearts and spleens were explanted. Whole blood and bone marrow were also extracted. GFP+ cells were quantified by FACS analysis. GFP+ and GFP-negative cells from heart samples were isolated and subjected to qPCR. (B) No GFP+ cells were detected in whole blood, bone marrow or spleens. However, in the corresponding hearts between 0.5% and 1% of MICs were present (exemplary FACS plots). Groups: Ctr WT (no OP): Wild-type mouse (C57Bl/6) without surgery. Ctr Nkx (sham OP): NkxCE-GFP mouse with sham operation. MI Nkx: NkxCE-GFP mouse with MI. (C) No CD45 gene expression was detected in MICs by qPCR, whereas GFP-negative cells from corresponding hearts (NegMI) showed low levels of CD45 and bone marrow served as positive control (n = 6 per group). *P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; (Kruskal–Wallis, postHoc: Dunn’s method). (D) Additionally, 1 week after MI, single-cell suspensions of infarcted hearts were stained for CD45 (exemplary plots). For Nkx (MI), one example with a high and one with a low number of GFP+ MICs is depicted. No GFP+ MICs were stained for CD45. (E) Summarized FACS results (see D, n = 4 per group). GFP+ MICs were detected not stained positive for CD45. (F) To verify if MICs originate from the heart itself hearts of C57Bl/6 wild type mice were harvested and transplanted into NkxCE-GFP recipients after 6 h of ischemia. Hearts were explanted after 1 week and GFP+ cells were quantified by FACS (n = 3). (G) No relevant number of GFP+ cells was detected either in transplanted WT or in transgenic recipient hearts (exemplary FACS plots). Groups: (1) Ctr Nkx (no OP): Nkx2.5-GFP mouse without surgery. (2) WT (HTX donor): Cervically transplanted heart of a wild type mouse (C57Bl/6). (3) Nkx (recipient): Heart of the Nkx2.5CE-GFP recipient mouse. (H) Summarized FACS results of cervical heart transplantation. The black line shows the number of GFP+ MICs detected after MI (groups see G). FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting.