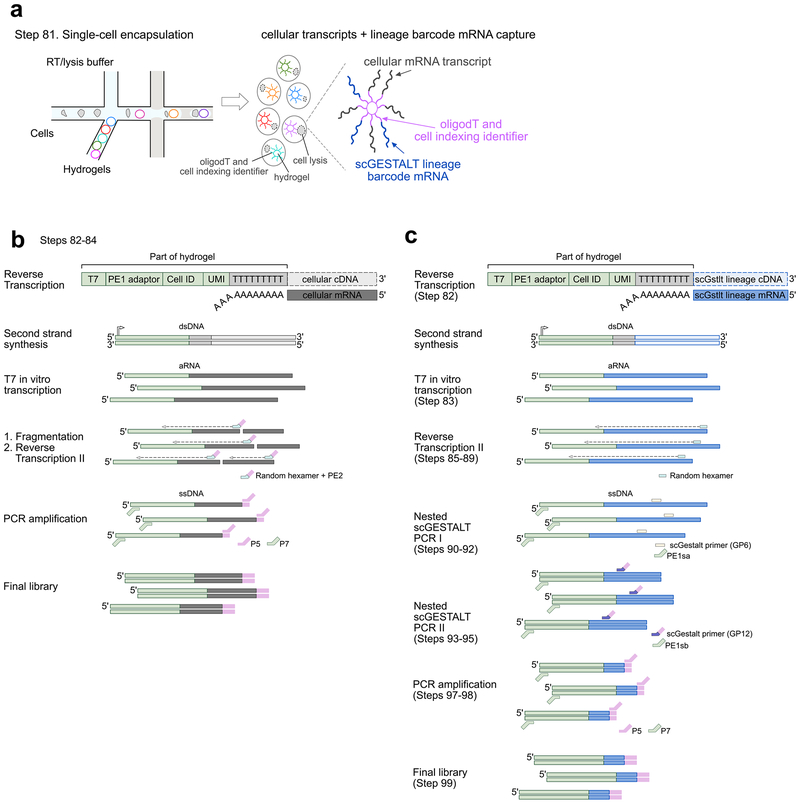
Figure 3. Transcriptome and scGESTALT library preparation overview.
a. Single cells are encapsulated and indexed in droplets using the inDrops platform (left, Step 82). Upon lysis (cells shown with dotted lines), polyadenylated cellular transcripts and scGESTALT lineage barcodes hybridize to oligodT primers on hydrogels. Hydrogels are color-coded to indicate distinct indexing identifiers. Adapted with permission from ref72.
b. Overview of transcriptome library preparation steps from single cells (Steps 82–84). Hydrogels are coated with oligonucleotides containing T7 promoter, an adaptor sequence (PE1), a cell indexing identifier (Cell ID), unique molecular identifier (UMI), and oligodT sequence. Polyadenylated cellular mRNA hybridizes to the oligodT sequence and is reverse transcribed into cellular cDNA sequence. Second strand synthesis is carried out to generate double stranded DNA (dsDNA) that is used for T7 in vitro transcription and generates linearly amplified RNA (aRNA). The aRNA is chemically fragmented and then subjected to a second round of reverse transcription using an oligonucleotide that contains a random hexamer and an adaptor sequence (PE2). The resulting single stranded DNA (ssDNA) is PCR amplified with Illumina P5 and P7 adaptor sequences containing overlap with PE2 and PE1 sequences, and a limited number of cycles to generate the final sequencing-ready transcriptome library. ssDNA fragments that do not contain the PE1 adaptor sequence will not be amplified.
c. Overview of scGESTALT lineage barcode library preparation steps from single cells. Polyadenylated lineage barcode mRNA, consisting of dsRed and edited scGESTALT CRISPR array (see Fig. 2, Step 33), are expressed from a transgene upon heat shock of the animal prior to brain dissection and dissociation. The lineage barcode mRNA hybridizes to oligodT sequence on the hydrogel and is reverse transcribed into lineage barcode cDNA. Second strand synthesis and T7 in vitro transcription is carried out similar to the transcriptome library preparation (Step 82). However, the aRNA is not fragmented in order to preserve the full lineage barcode sequence (Step 83, part of the of reverse transcribed product is not fragmented and stored at −80 °C). Instead reverse transcription is carried out using random hexamers to generate full-length ssDNA (Steps 85–89). The edited scGESTALT CRISPR array sequence is selectively enriched from the full-length ssDNA using a nested PCR approach. The first round amplifies a longer piece of dsDNA using a primer that hybridizes in the dsRed sequence (GP6) and one that overlaps the PE1 adaptor sequence (PE1sa) (Steps 90–92). The resulting dsDNA is used in a second round to target the edited lineage barcode sequence using a primer that binds upstream proximal to the start of the CRISPR lineage array sequence (GP12) and a primer that overlaps the adaptor sequence (PE1sb) (Steps 93–95). The resulting dsDNA is PCR amplified (Steps 97–98) similar to the transcriptome library preparation to generate the final sequencing-ready scGESTALT lineage barcode library (Step 99).