Figure 2.
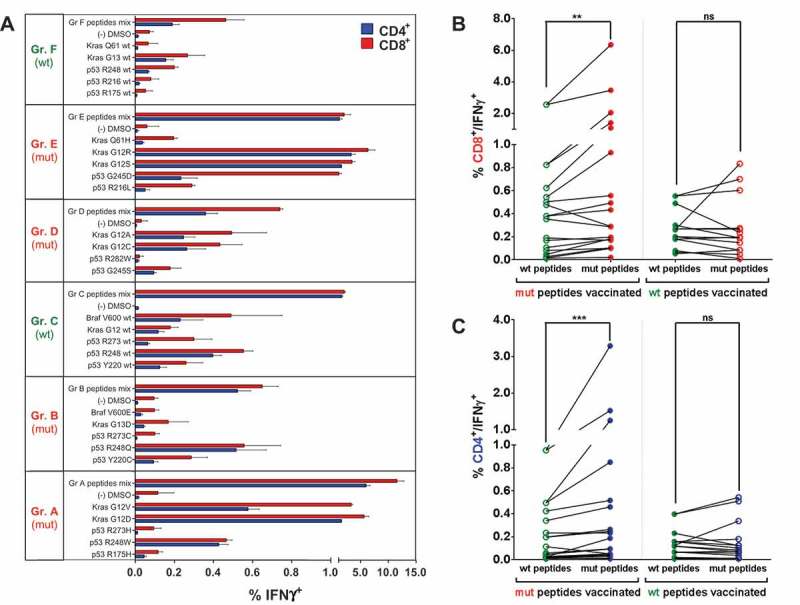
Mutation-specific, polyvalent CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses after vaccination with mutated and wt p53 and Kras derived peptides. (A) Overview of recall responses against all peptides tested in HLA-humanized A2.DR1 dtg mice immunized with different long peptide cocktails. Six cohorts of mice were immunized with one group of mutated (mut) or wild-type (wt) peptides (A to F), each, in PBS-based formulations including 50 μg of CpG ODN 1668 as an adjuvant, twice on a bi-weekly bases. In vitro recall responses were obtained from combined IFN-γ secretion assays and intracellular cytokine stainings performed with CD90+ purified T cells from immunized mice. IFN-γ secretion of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells upon in vitro recall against single peptides of each respective mix (single) and against whole peptide mixes (mix) presented by CD11c+ DCs are displayed. Each peptide, peptide mix and control sample was tested in triplicates. Results are plotted as means of triplicate assays ± SEM. Data obtained from one of two identical lines of experiments are shown. (B)/(C) Mutation specific responses after vaccination of A2.DR1 dtg mice with mutated peptides. Percentages of IFN-γ secreting splenic CD8+ (B) and CD4+ (C) T cells upon in vitro recall against mutated (mut) and wild-type (wt) peptides represented on CD11c+ DCs. Results were accumulated from six cohorts of mice immunized with one group of mutated (mut) or wild-type (wt) peptides (A to F, see Figure 2 (A)). Means of mutated and wt peptide triplicates are plotted and groups were tested for differences by applying two-tailed Wilcoxon signed rank test. Representative data obtained from one of two identical lines of experiments are shown. Filled dot symbols: peptides used for vaccination and in vitro recall response testing, open dot symbols: peptides used for in vitro recall response testing only, ns: not significant.
