Figure 5.
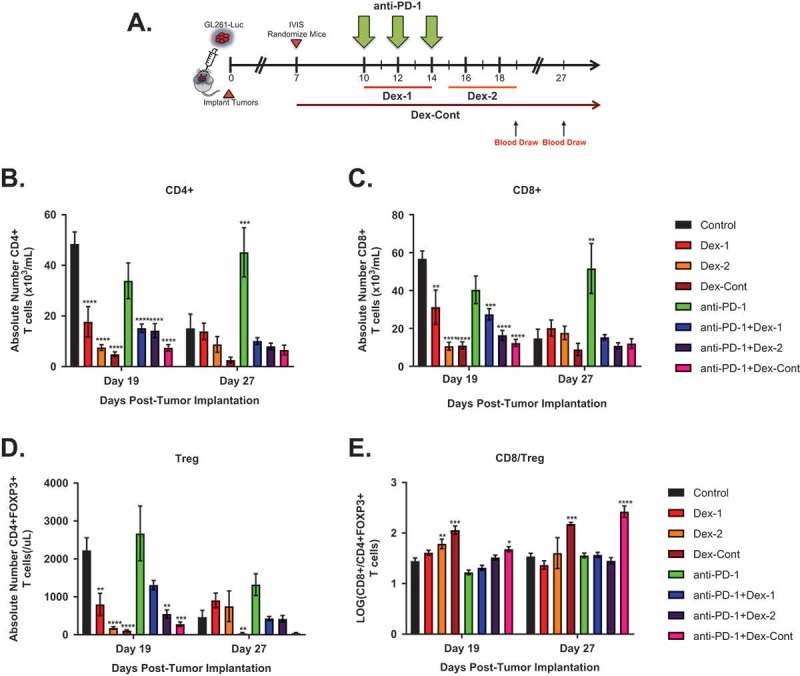
Dexamethasone alone or combined with anti-PD-1 therapy significantly alters peripheral T cell compartments in mice bearing intracranial glioma tumors. (A) Timeline of blood draws relative to treatment schedule in the intracranial GL261-Luc experiment (N = 80, 10 mice/group): Blood was collected from the retro-orbital venous plexus of each mouse on days 19 and 27. Depicted are absolute numbers of (B) CD4+, (C) CD8+, (D) CD4+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Treg), and (E) CD8/Treg ratios in peripheral blood by treatment group. Dexamethasone treatment, either alone or in combination with anti-PD-1 therapy, resulted in persistent reductions within CD4+, CD8+, and Treg compartments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. If no asterisks are shown, statistical analyzes yielded non-significant P-values.
