Figure 1.
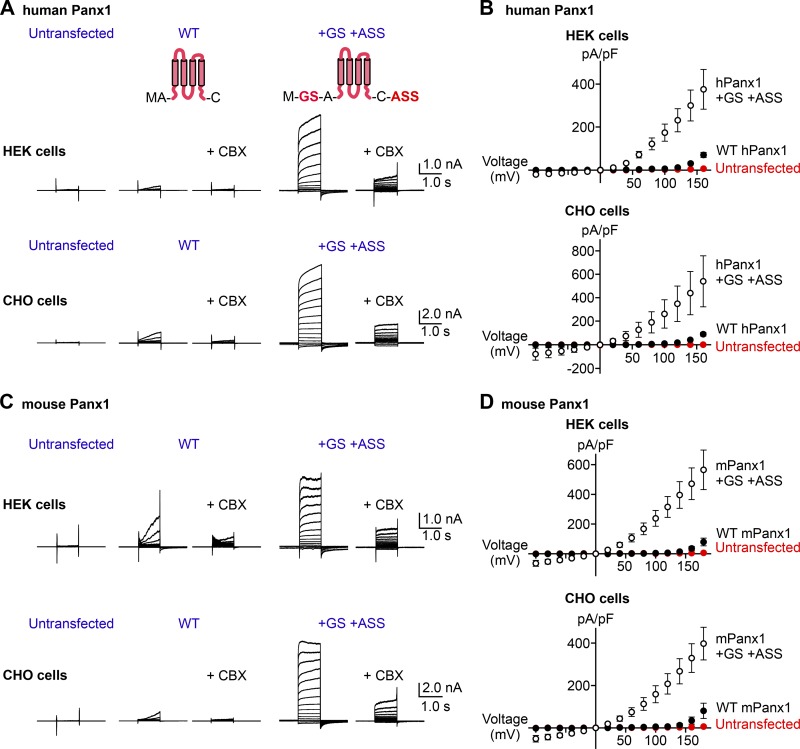
Adding a few amino acids at the Panx1 termini augments voltage-dependent channel activity. (A) Whole-cell current recordings of voltage-clamped HEK cells (top) or CHO cells (bottom) expressing hPanx1. Shown are representative recordings of at least 10 different cells untransfected (left), transfected with WT hPanx1 (middle), or transfected with hPanx1+GS/+ASS (right). Cells were held at −60 mV and stepped between −100 mV and +160 mV for 1.0 s in 20-mV increments. CBX (50 µM) was applied using a rapid solution exchanger. Cartoons represent Panx1 topology and construct modifications. (B) Current density–voltage plots of hPanx1 constructs expressed in HEK cells (top) or CHO cells (bottom). (C) Whole-cell current recordings of HEK cells (top) or CHO cells (bottom) expressing mPanx1. Cells were either untransfected (left), transfected with WT mPanx1 (middle), or transfected with mPanx1+GS/+ASS (right). Shown are representative recordings from at least five different cells. (D) Current density–voltage plots of mPanx1 constructs expressed in HEK cells (top) or CHO cells (bottom). Each point represents the mean current density at each voltage, and bars represent SEM.