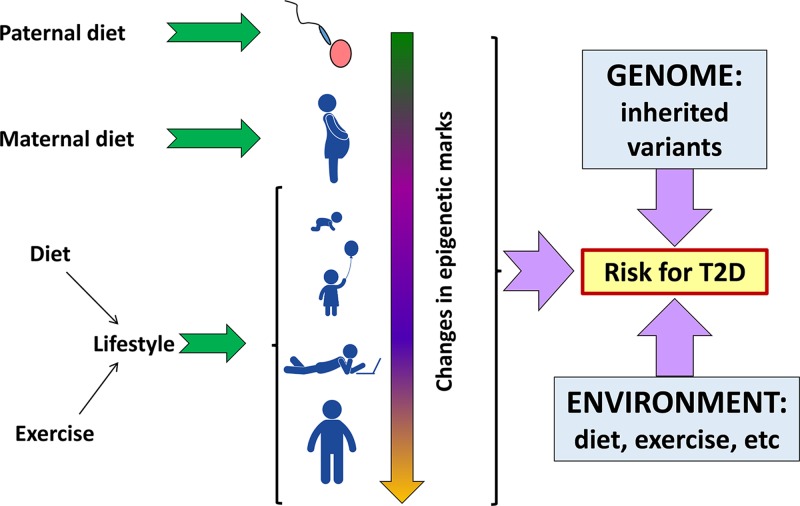
Figure 30. Many factors, environmental, genetic and epigenetic interact together in the overall risk for T2D.
Epigenetic factors can alter throughout the life of an individual, and may be affected by parental environment preconception, and maternal environment during pregnancy. A multitude of inherited variants (some of which may be protective) combine with epigenetic status to generate an overall genetic risk for T2D, but the disease state will generally only be manifested in the presence of environmental triggers. Although inherited genetic variants are hard to change, it is apparent that environmental change (improved diet and more exercise) may impact on disease severity not only directly, but also indirectly by epigenetic changes. Pictograms from PictArts.