Figure 5: CCR2 is required for AM localization within TB granulomas.
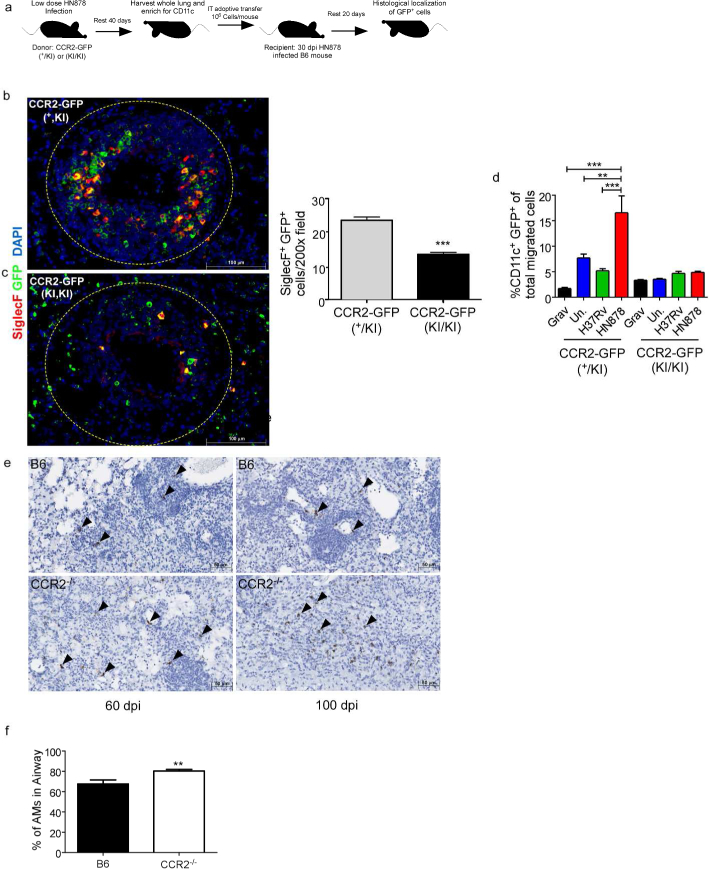
(a) CD11c+ cells were purified from lungs of 30 dpi HN878-infected CCR2-GFP(+/KI) or CCR2-GFP(KI/KI) mice and 106 cells were IT transferred into B6 HN878-infected mice (n=5) at 30 dpi.(a-c) Lungs were harvested at 50 dpi and examined for localization of SiglecF+ GFP+ cells within TB granulomas using the morphometric tool of the Zeiss Axioplan microscope. (d) CCR2-GFP(+/KI) or CCR2-GFP(KI/KI) BMDMs were stimulated in vitro with 20 μg/mL irradiated Mtb HN878 for 24 hours. Migration towards uninfected, H37Rv- or HN878-infected epithelial cell supernatants was analyzed via transwell chemotaxis assays and flow cytometry (n=3). (e) Ccl2 mRNA localization was determined within FFPE lung sections from B6 and CCR2−/− HN878-infected using RNAScope in situ hybridization (ISH). Arrows point to Ccl2 mRNA localization(brown). (f) B6 and CCR2−/− mice (n=5) were infected with HN878 and percentage of AMs with airway label CD45.2 delivered IT was calculated on 14 dpi by flow cytometry. Grav=Gravity control, Un.=uninfected, AMs=Alveolar Macrophages. n=5 (b,c) Student’s t-test. n=3, (d) 2-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest. (f) Student’s t-test.
