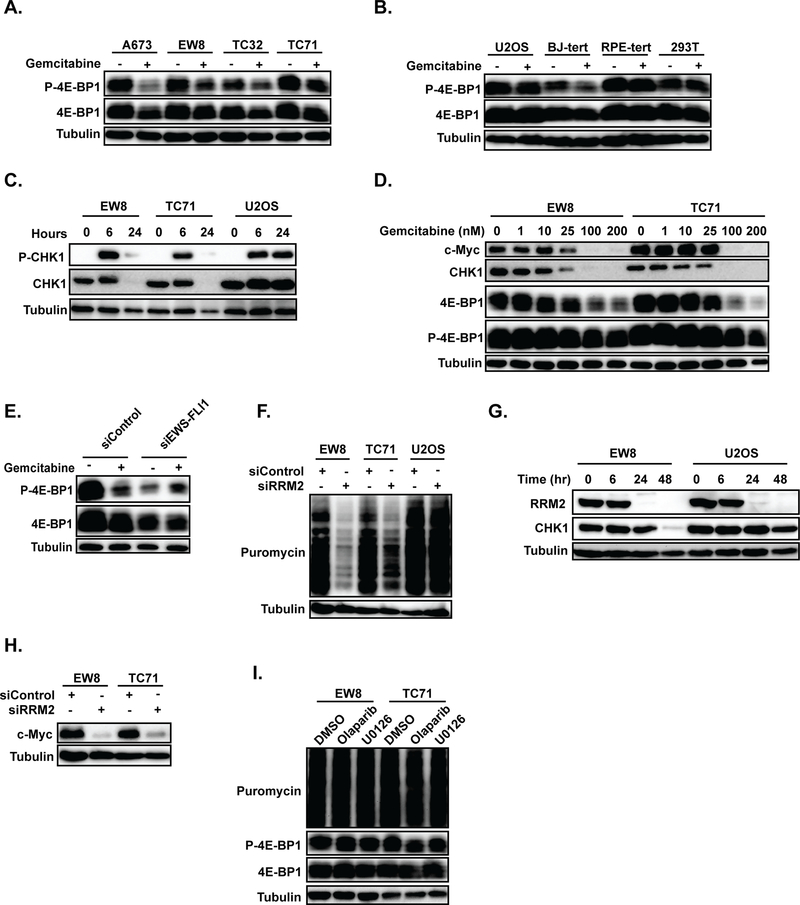
Figure 6.
Gemcitabine reduces the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 in Ewing sarcoma cells. (A, B) Immunoblot for p-4E-BP1–37/46 and total 4E-BP1 in Ewing sarcoma (A) and control (B) cell lines treated with gemcitabine. Cells were treated with 100 nM gemcitabine for six hours, allowed to recover for 18 hours, and then subjected to immunoblotting. (C) Immunoblot for p-CHK1–345 and total CHK1 in Ewing sarcoma and osteosarcoma cells treated with gemcitabine, as described in (A). Lysates were collected at 0, 6, and 24 hours after drug was added. (D) Immunoblot showing the dose-dependent effects of gemcitabine on c-Myc, CHK1, 4E-BP1, and p-4E-BP1–37/46. (E) EWS-FLI1 was knocked down in A673 cells using siRNA and then the effect of gemcitabine on phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 was assessed using immunoblotting. (F) Protein synthesis was assessed, using puromycin labeling, in Ewing sarcoma and osteosarcoma cells treated with siRNA targeting RRM2 (siRRM2) or a control siRNA (siControl). (G, H) Immunoblot for total CHK1 (G) and c-Myc (H) in cells treated with siRRM2. In all immunoblots, protein loading was normalized using cell number. (I) EW8 and TC71 cells were treated with olaparib (5 μM) or U0126 (5 μM) for 24 hours and then protein synthesis was assessed using puromycin labeling.