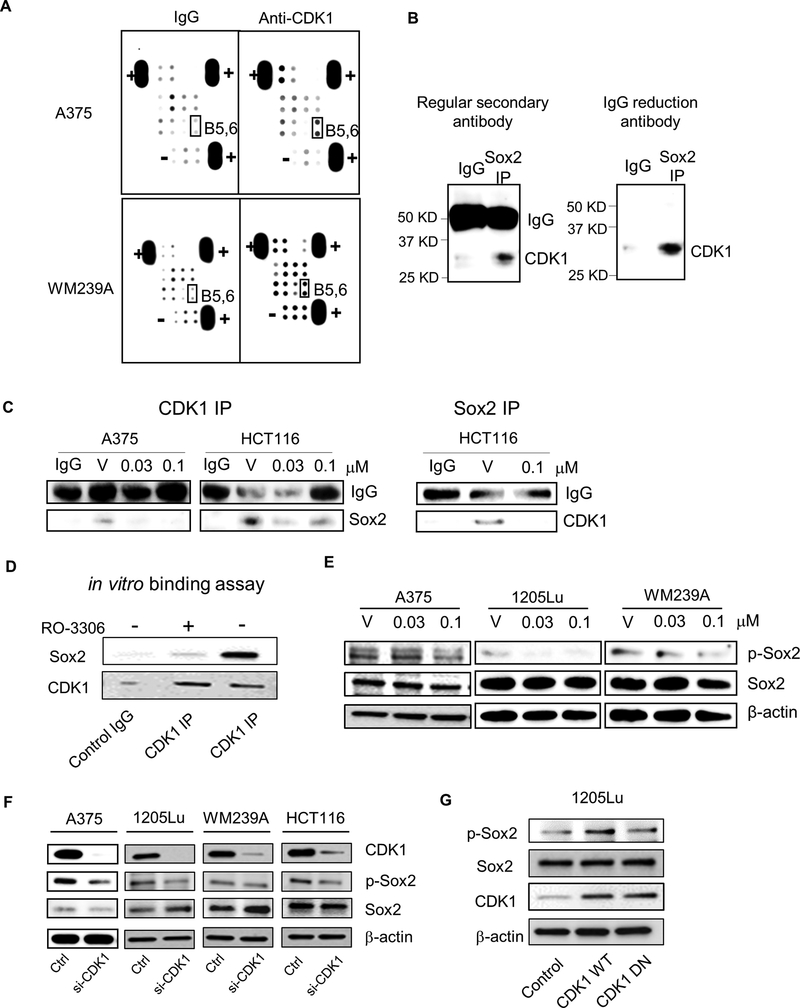
Figure 4. Identification of stem cell genes binding to CDK1.
A, Stem cell gene antibody array. Lysates of A375 and WM239A cells were IP pulled-down by IgG (control) or anti-CDK1 antibody, and subjected to the antibody array. B5,6, highlighted in black box, are Sox2. “+” and “-” represent positive and negative control, respectively. B, Sox2 IP immunoblotted by anti-CDK1 antibody in colon cancer cell line HCT116. Left panel, immunoblot with anti-rabbit secondary antibody, Right panel, immunoblot with rabbit IgG reduction TrueBlot® secondary antibody. C, CDK1 and Sox2 IP immunoblot of cells treated with vehicle (V) or RO-3306. Left panel, Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-CDK1 antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Sox2 antibody. Right panel, Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Sox2 antibody and immunoblotted with anti-CDK1 antibody. IgG served as internal control. D, Immunoblots depicting the binding of recombinant Sox2 to CDK1/Cyclin B Complex after CDK1 IP. RO3306 was used to show CDK1-dependent interaction. E, Immunoblots depicting the Sox2 phosphorylation (S249-S250-S251, p-Sox2) and Sox2 after treatment with vehicle (V) or RO-3306 (0.03 or 0.1 μM) in A375, 1205Lu and WM239A cells. β-actin used as loading control. F, Immunoblots depicting Sox2 phosphorylation (p-Sox2) and Sox2 after CDK1 siRNA knockdown in A375, 1205Lu, WM239A and HCT116 cells. G, Immunoblots depicting phosphorylated Sox2 (p-Sox2), Sox2 and CDK1 in 1205Lu cells transfected with Control, CDK1 WT and CDK1 DN vectors.