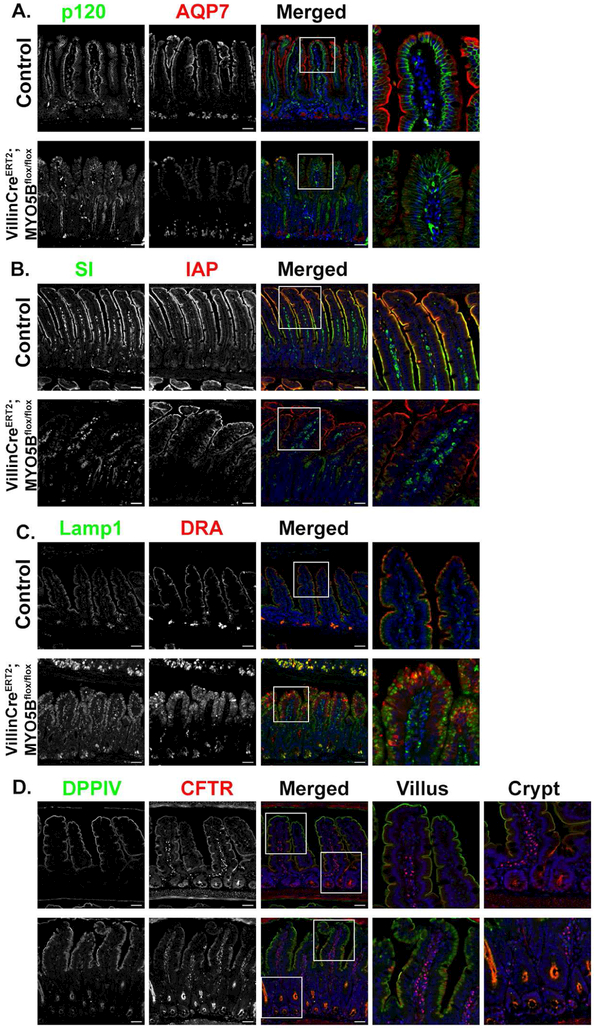
Figure 6: Loss of MYO5B in adult mice leads to decreased apical expression of SI, AQP7 and DRA, but preservation of CFTR.
(A) Immunostaining for p120 (green) and AQP7 (red) in control mice showed proper apical localization of AQP7. Tamoxifen-treated VillinCreERT2MYO5Bflox/flox mice lost apical expression of AQP7. (B) In control mice IAP (red) and SI (green) were both expressed on the apical membrane of of enterocytes. In VillinCreERT2MYO5Bflox/flox tamoxifen-treated mice SI was greatly reduced on the apical membrane and most SI appeared to be intracellular. IAP remained at the tips of the villi in VillinCreERT2MYO5Bflox/flox but also showed a subapical staining pattern through much of the villi (C) Immunostaining for DRA showed loss of apical DRA in tamoxifen-treated VillinCreERT2;MYO5Bflox/flox mice. (D) CFTR (red) and DPPIV (green) immunostaining in control mice demonstrated apical expression. In VillinCreERT2MYO5Bflox/flox CFTR was present below the apical membrane in the villi, however CFTR was also present on the apical membrane and appeared to be highly expressed in the crypts. n=4-6 mice per group, scale bars=50 μm.