Figure 3. The two cranial (C2-C3 & C3-C4) motion segments (n = 9/level) have different axial response than the two most caudal levels (C5-C6 & C6-C7).
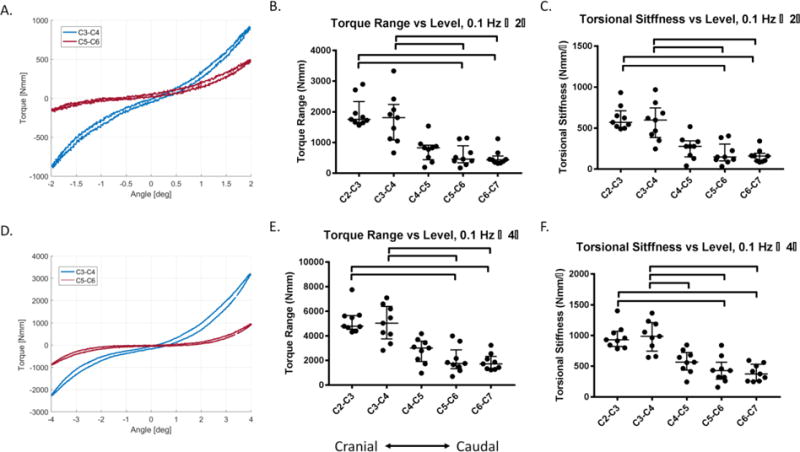
(A) The force displacement curve of a C3-C4 motion segment has lower range of motion (ROM) and lower tensile compliance than the C5-C6 motion segment from the same animal. (B) The axial ROM of C2-C3 & C3-C4 were significantly lower than C5-C6 & C6-C7, and the ROM of C2-C3 was significantly lower than C4-C5. (C) The tensile compliance for C2-C3 was significantly lower than C5-C5 and C6-C7, and C3-C4 was significantly lower than C6-C7 but was only a trend lower than C5-C6 (p = 0.09). There were no differences in compressive compliance between levels. Lines are median, error bars are interquartile range and bars indicate significant difference (p < 0.05).
