Figure 6. NRF2 ubiquitination and protein stability is regulated by PIM1 kinase.
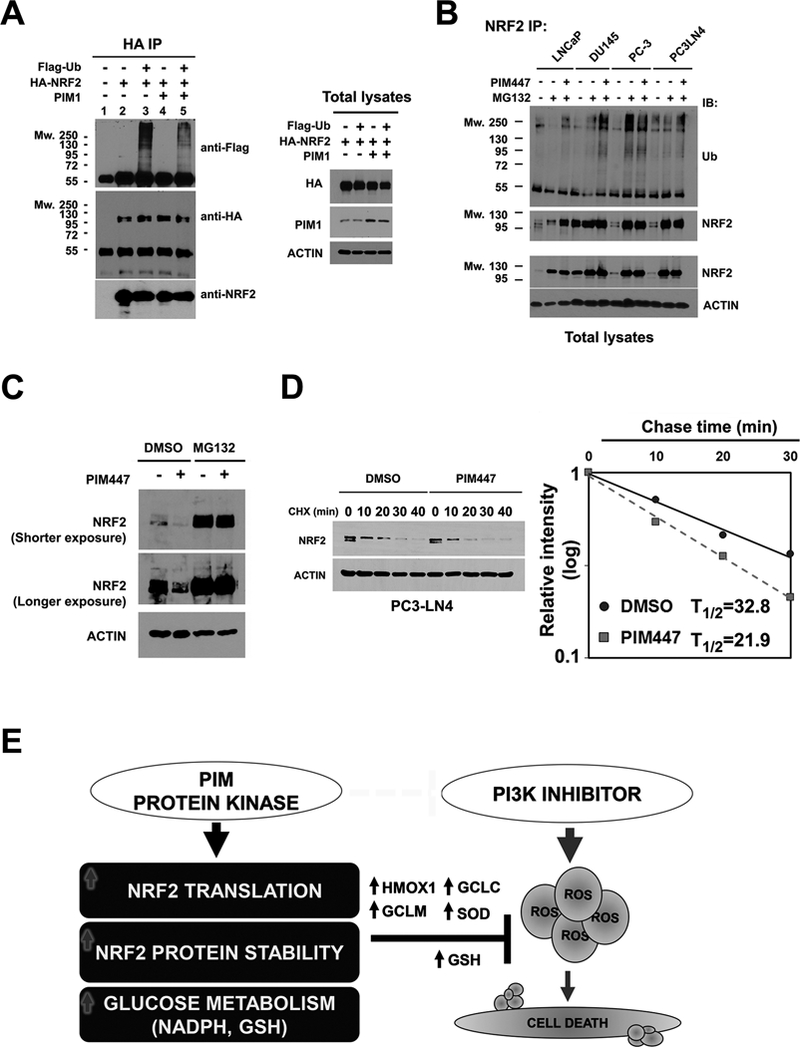
(A) Immunoblot analysis of ubiquitinated NRF2 protein. LNCaP cells were transfected with Flag-Ub, HA-NRF2, and PIM1 as indicated. After 48 hr, these transfectants were exposed to 10 μmol/L MG132 for 4 hr. NRF2 was immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody, and was subjected to immunoblot analysis with an anti-Flag antibody used for detection of ubiquitylated NRF2. An aliquot of the total lysate was evaluated for immunoblot analysis.
(B) Immunoblot analysis of endogenous NRF2 ubiquitination. Following exposure to MG132 total extracts from LNCaP, DU145, PC-3 and PC3-LN4 cells were immunoprecipitated with an anti-NRF2 antibody. Immunoprecipitated NRF2 was subjected to immunoblot analysis with an anti-ubiquitin (anti-Ub) antibody for detection of endogenous ubiquitylated NRF2. An aliquot of the total cell lysate was used for immunoblot analysis.
(C) Immunoblot analysis of NRF2 accumulation after MG132 treatment. PC3-LN4 cells were treated with 3 μmol/L PIM447 for 24 hr in the presence or absence of 10 μmol/L MG132.
(D) The half-life of NRF2 in PC3-LN4 cells following treatment with DMSO or 3 μmol/L PIM447. After 24 hr treatment, cells were exposed to 10 μg/ml Cycloheximide for the indicated times. Total lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis. NRF2 and Actin levels were determined by densitometry, and the level of NRF2 relative to that of Actin was plotted as a function of time to determine the decrease in NRF2 protein.
(E) Schematic outline of the resistance mechanism induced by PIM kinase. Expression of the PIM protein kinase induces tumor resistance to PI3K inhibitors. PIM promotes NRF2 synthesis through phosphorylation of eIF4B (S406) and increases NRF2 activity by inhibiting ubiquitination-mediated proteasome degradation. PIM modulates glycolytic metabolism to favor a decrease in ROS accumulation by producing NADPH and GSH. Genetic depletion of ROS scavenger proteins overcomes PIM-mediated drug resistance. Combining PIM and PI3K inhibitors promotes cancer death by inhibition of NRF2 signaling.
