Fig. 3. Effects of CDK8 inhibition at different stages of liver metastatic growth.
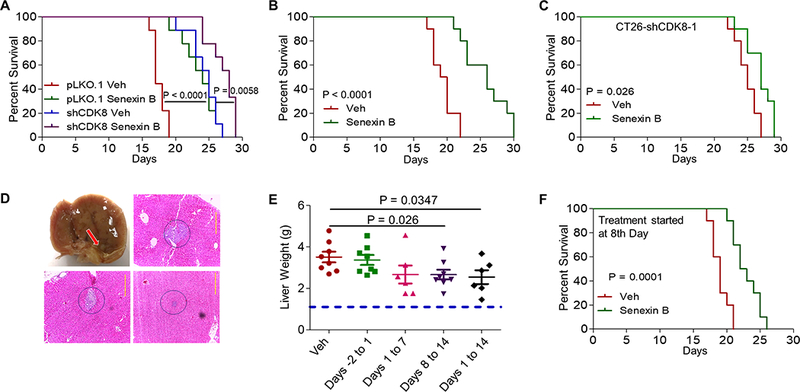
(A-C) Survival studies, Kaplan-Meier plots (n = 10 in all experiments). (A) pLKO.1 control and shCDK8–1 cell lines, treated with vehicle or Senexin B (oral b.i.d). (B) Parental CT26 cells treated with vehicle or Senexin B (diet + oral). (C) CT26-shCDK8–1 cells treated with vehicle or Senexin B as in (B). (D) Metastatic tumors in the livers of mice euthanized 7 days after splenic inoculation of CT26 cells, detectable macroscopically (upper left, tumor marked with arrow) and microscopically. Representative examples are shown. Scale bars: 0.2 mm. (E) Effects of Senexin B treatment at different stages of liver metastasis on tumor growth in liver. Mice (n=10) were treated with Senexin B (oral b.i.d.) over two days prior to splenic inoculation, during the first week after inoculation, during the second week after inoculation, or over two weeks after inoculation of CT26 cells. (F) Mouse survival study conducted as in (B) except drug treatment was initiated on day 8 after inoculation.
