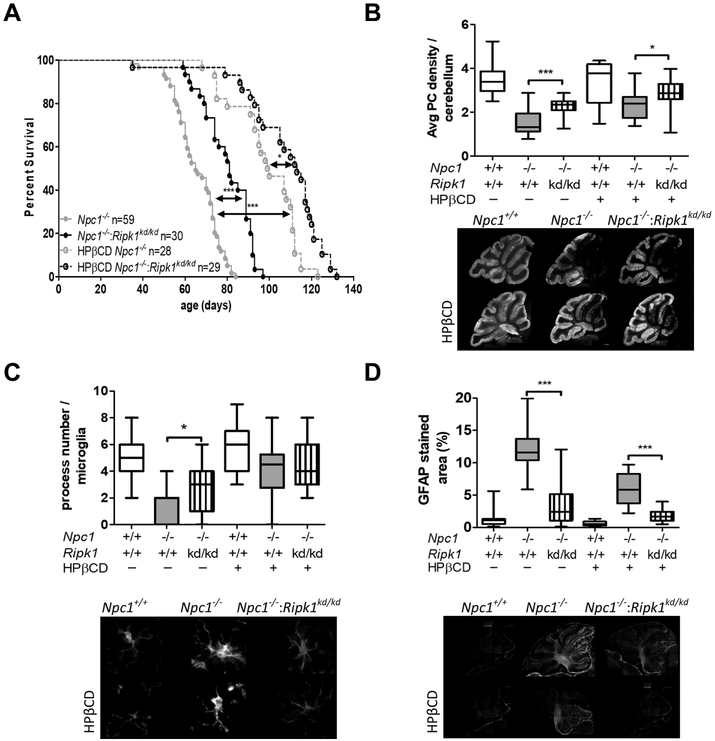
Figure 3. Characterization of Npc1−/−:Ripk1kd/kd double mutant mice.
A) Survival was significantly increased (p<0.001) in Npc1−/−:Ripk1kd/kd (n=30) mice compared to Npc1−/−(n=59) mice on the same mixed C57B1/6 and Balb/c genetic background. Survival was also increased in Npc1−/− mice treated with 4000 mg·kg−1 of HPβCD (n=28, p<0.001). Consistent with an additive effect, survival was further increased in Npc1−/−:Ripk1kd/kd mice treated with 4000 mg·kg−1 of HPβCD (n=29, p<0.05). B) Average cerebellar Purkinje neuron density per 100 μM was increased toward normal in Npc1−/−:Ripk1kd/kd mice and further increased in Npc1−/−:Ripk1kd/kd mice treated with HPβCD. Representative calbindin 28K stained sagittal sections are shown below the graphs. C) Quantification of microglial processes were consistent with a decreased activated morphology in Npc1−/−:Ripk1kd/kd mice compared to Npc1−/− mice (p<0.05). No difference was observed in HPβCD treated animals. D) GFAP staining decreased toward normal in Npc1−/−:Ripk1kd/kd mice compared to Npc1−/− mice (p<0.001), and consistent with an additive effect, decreased further in HPβCD treated animals (p<0.001). For B, C and D data were obtained from three sagittal sections obtained from six animals corresponding to each genotype. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, Mann-Whitney test was used to compare means. Log-Rank Mantel-Cox test was used to compare survival curves.