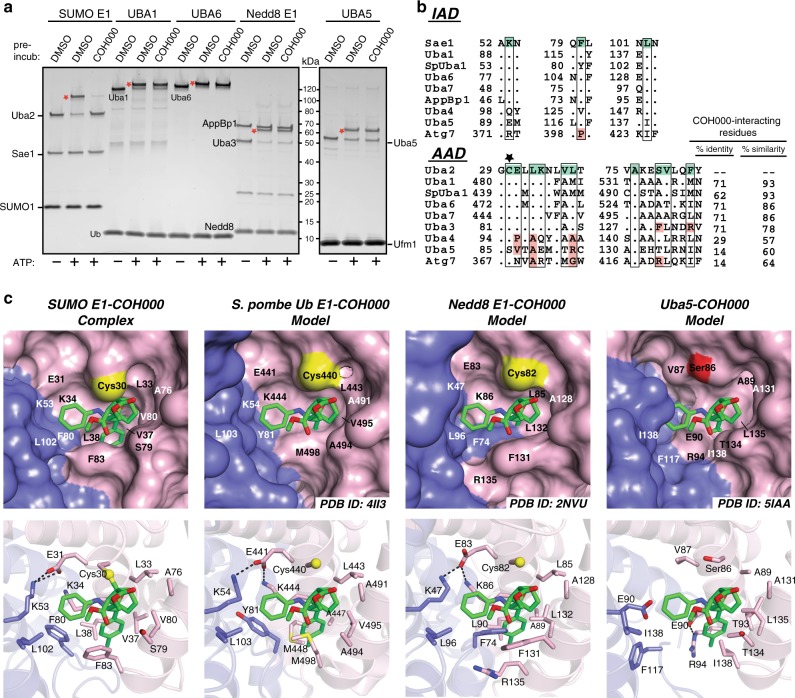
Fig. 5.
Insights into the molecular basis of COH000 specificity for SUMO E1. a In vitro E1–Ubl thioester formation assays were performed as described in the Methods. The samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and visualized with Sypro Ruby stain. The E1–Ub thioester products are indicated with a red star. b Structure-based sequence alignment of the COH000-interacting region of the indicated Ub and Ubl E1 enzymes. Residues involved in contacts to COH000 in the SUMO E1COH000 structure are shaded green and the cysteine residue that forms the thioether bond with COH000 (Cys30) is indicated with a black star. Residues of other Ubl E1s at positions corresponding to the COH000 binding site of SUMOE E1 that are identical are indicated by periods and those that harbor different physicochemical properties are shaded red. The percent identity and similarity of Ubl E1 residues corresponding to the COH000 binding site of SUMO E1 are shown to the right of the alignment. ‘Sp’ stands for S. pombe. c Models of Ubl E1-COH000 complexes were created by superimposing the adenylation domains of Ubl E1s onto the SUMO E1COH000 structure. c (top) The indicated Ubl E1 structures are shown as surface representations with a magnified view of the region corresponding to the COH000-interacting pocket observed in the SUMO E1COH000 structure. The g1/g2 regions of the Ubl E1s are not shown because they occlude the cryptic COH000 binding pocket. The SUMO E1COH000 structure is shown in the same orientation in the left panel for comparison. Cys30 of SUMO E1 and the corresponding cysteines/serines of other Ubl E1s are colored yellow and red, respectively. Ubl E1 residues corresponding to the COH000 binding site of SUMO E1 are labeled. c (bottom) The structures are shown as cartoon representations with Ubl E1 residues corresponding to the COH000 binding site of SUMO E1 shown as sticks and labeled