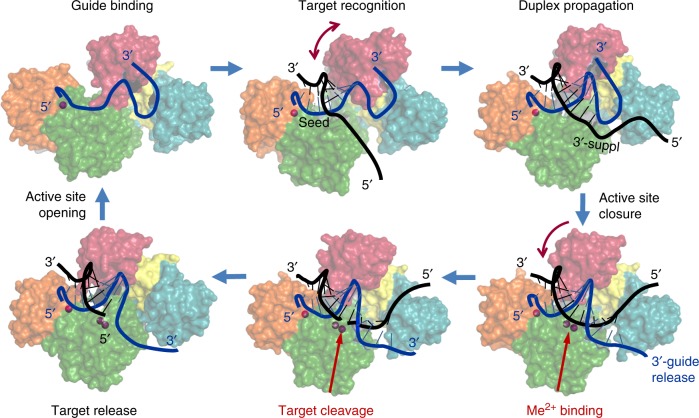
Fig. 2.
The catalytic cycle of Ago proteins. Guide-loaded Ago performs search for a complementary target through base-pairing with the seed region of the guide strand, followed by duplex propagation through the central part and the 3′-supplementary site of the guide, thus checking for possible mismatches. Conformational mobility of the PAZ domain (shown by arc-shaped arrows) likely facilitates correct base-pairing, through controlled release of the guide 3′-end and active site closure. Conformational changes in the active site allow binding of catalytic metal ions, followed by cleavage of the target strand and its stepwise release from the complex. The drawings are based on the structures of TtAgo at different steps of its functional cycle (PDBs, from the upper left corner, clockwise: 3DLH, 3F73, 4N41, 4NCB, 4NCA, 4N76, see Supplementary Fig. 2). The guide strand is blue, the target strand is black; only the target strand of DNA substrate is shown (the structure of complexes with double-stranded DNA remains unknown for any pAgo)