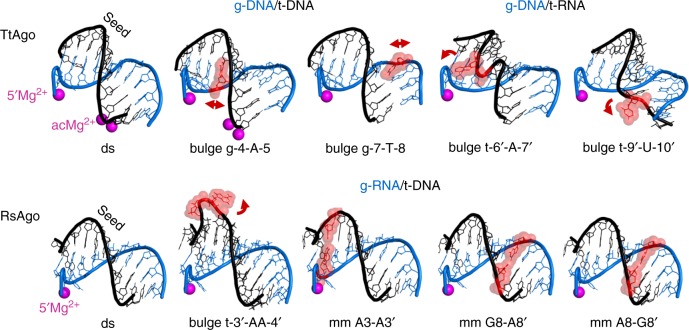
Fig. 4.
Accommodation of helical imperfections in the ternary complexes of pAgo proteins. Structural features of the duplexes formed in the seed region in ternary complexes of TtAgo71 (upper raw) and RsAgo51 (bottom) containing bulges or mismatches (shown in red) in the guide or target strand, in comparison with fully double-stranded duplex (“ds”). Only the part of the duplex between the guide 5′-end and the active site in the PIWI domain is shown (guide positions 1 through 10–12 for various complexes); Mg2+ ions bound in the MID-pocket (5′Mg2+) and in the active site (acMg2+) are indicated; some complexes of TtAgo were obtained with a catalytically inactive mutant and thus lack catalytic metal ions. The distortions of the double-helix are shown with red arrowheads; the nucleotide bulges can be either stacked-in (bulges in the guide strand; g-4-A-5 and g-7-T-8 in TtAgo) or flipped-out of the duplex (bulges in the target strand; t-6′-A-7′, t-9′-U-10′ for TtAgo, t-3′-AA-4′ for RsAgo). The ternary complexes were obtained with g-DNA/t-DNA or g-DNA/t-RNA for TtAgo, or g-RNA/t-DNA for RsAgo, as indicated. The PDB accession numbers are (from left to right): TtAgo, 4NCB, 5XP8, 5XOU, 5XOW, 5XPA; RsAgo, 6D8P, 6D8A, 6D92, 6D9L, 6D9K. See Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. 3 for full description of each complex