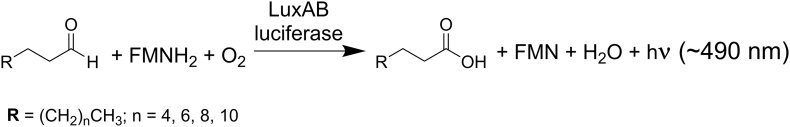
Scheme 1.
General reaction mechanism of bacterial bioluminescence. Long-chain aldehydes (CH3(CH2)nCHO), reduced flavin mononucleotide (FMNH2) and molecular oxygen (O2) are converted by the enzyme luciferase (LuxAB) to the corresponding long-chain acids (CH3(CH2)nCOOH), oxidized flavin mononucleotide (FMN), water (H2O) and light emission (hν) with an approximate maximum at 490 nm.