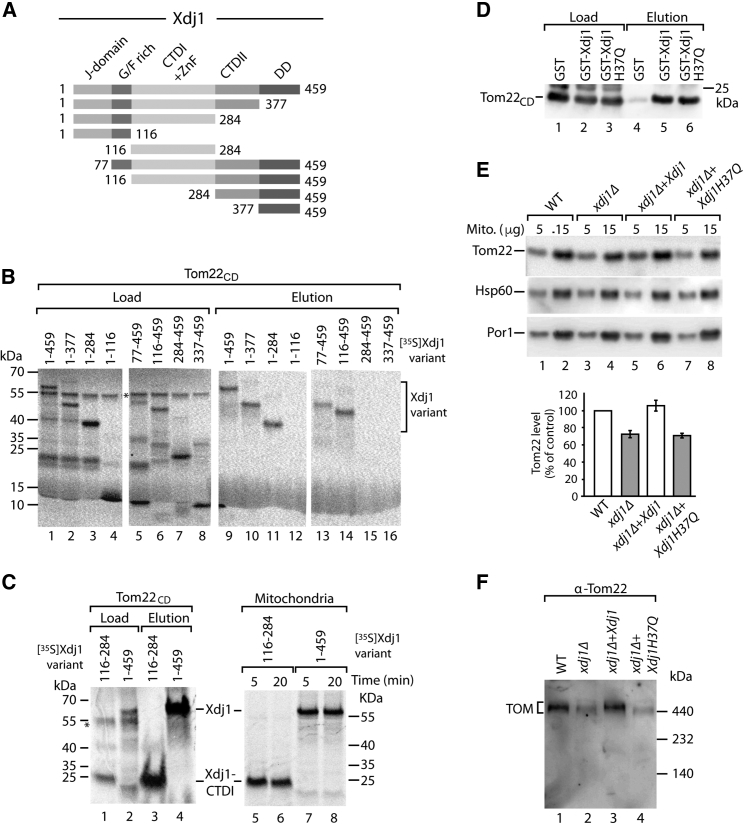
Figure 4.
The Barrel Domain CTD1 of Xdj1 Binds to Tom22 and the J-Domain Promotes Protein Biogenesis
(A) Schematic view of truncated Xdj1 constructs. J-domain; G/F rich, glycine/phenylalanine rich domain; CTDI + II, C-terminal (barrel) domains I, II; ZnF, zinc finger-like region; DD, dimerization domain.
(B) Xdj1 constructs were incubated with Tom22CD coupled to Ni-NTA. Load and elution fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Load was 5%; elution was 50%.
(C) Left panel, 35S-labeled Xdj1-CTDI and full-length Xdj1 were incubated with Tom22CD coupled to Ni-NTA. Load (5%) and elution (100%) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Right panel, Xdj1-CTDI and Xdj1 were incubated with isolated mitochondria. Mitochondria-bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography.
(D) Tom22CD was incubated with glutathione columns coated with GST, GSTXdj1, or GSTXdj1-H37Q. Load (2%) and elution (100%) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunodetection with Tom22-specific antiserum.
(E) Mitochondria from wild-type (WT), xdj1Δ, and xdj1Δ strains expressing plasmid-encoded XDJ1 or XDJ1-H37Q were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunodetection. Quantification of Tom22 levels, mean values ± SEM (n = 3); the amount in WT mitochondria was set to 100% (control).
(F) Mitochondria from WT, xdj1Δ, and xdj1Δ strains expressing XDJ1 or XDJ1-H37Q were analyzed by blue native electrophoresis and immunodetection.
See also Figure S4.